Effects of Ezrin and Heat Shock Protein 70 on Apoptosis and Proliferation of Human Osteosarcoma Cells
- PMID: 26311104
- PMCID: PMC6583739
- DOI: 10.1111/os.12186
Effects of Ezrin and Heat Shock Protein 70 on Apoptosis and Proliferation of Human Osteosarcoma Cells
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the influence of knocking down ezrin expression in combination with heat shock protein (HSP)-induced immune killing on the apoptosis and proliferation of mouse osteosarcoma cells.
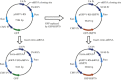
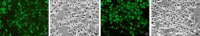
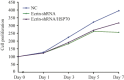
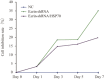
Methods: The HSP70 and ezrin-shRNA DNA fragments cloned into the expression vector pGFP-V-RS and the expression vectors pGFP-V-RS-shRNA and pGFP-V-RS-shRNA-HSP70 constructed and transfected into MG63 cell line, where their status was observed by fluorescent microscopy. Expression of ezrin and HSP70 was determined by RT-PCR and western blot. Changes in cell apoptosis and proliferation were assessed by flow cytometry and MTS and changes in expression of apoptosis and cell cycle-related proteins by western blot. Specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) were induced by HSP70 and its lethal effect on target MG63 tumor cells analyzed by MTS assay.
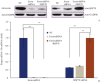
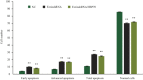
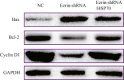
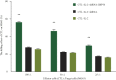
Results: The specific vector simultaneously downregulated ezrin and upregulated HSP70. Compared with ezrin knockdown alone, simultaneous HSP70 overexpression partially recovered the promoted cellular apoptosis and proliferation suppression by induced by ezrin knockdown; however, the apoptosis rate of MG63 cells was significantly greater than that of a negative control. In addition, ezrin-shRNA and ezrin-shRNA/HSP70 promoted expression of Bax. However, expression of these agents reduces Bcl-2 and Cyclin D1. The cytotoxic effects of CTLs on target MG63 tumor cells were significantly greater in the CTL + IL-2 + HSP70 group than the CTL + IL-2 group.
Conclusions: Simultaneously knocking down ezrin and overexpressing HSP70 promotes apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of osteosarcoma cells and HSP70 induces CTL, enhancing the lethal effect on tumor cells.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Ezrin; Heat shock protein 70; Osteosarcoma; Proliferation.
© 2015 Chinese Orthopaedic Association and Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of ezrin-shRNA in combination with HSP70 on the apoptosis and proliferation of osteosarcoma cells.Oncol Lett. 2016 Nov;12(5):3441-3448. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5103. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27900018 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus-mediated small interfering RNA targeting ezrin induces apoptosis and inhibits metastasis of human osteosarcoma MG-63 cells.Biosci Rep. 2018 Aug 29;38(4):BSR20180351. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180351. Print 2018 Aug 31. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29899165 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-144 inhibits the proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and migration of osteosarcoma cell line F5M2.Tumour Biol. 2015 Sep;36(9):6949-58. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3396-0. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25854173
-
The prognostic value of elevated ezrin in patients with osteosarcoma.Tumour Biol. 2014 Feb;35(2):1263-6. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-1168-2. Epub 2013 Sep 7. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24014052
-
Osteosarcoma metastasis: prospective role of ezrin.Tumour Biol. 2014 Jun;35(6):5055-9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-1799-y. Epub 2014 Mar 9. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24609902 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of ezrin-shRNA in combination with HSP70 on the apoptosis and proliferation of osteosarcoma cells.Oncol Lett. 2016 Nov;12(5):3441-3448. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5103. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27900018 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacologic Inhibition of Ezrin-Radixin-Moesin Phosphorylation is a Novel Therapeutic Strategy in Rhabdomyosarcoma.Sarcoma. 2020 Sep 9;2020:9010496. doi: 10.1155/2020/9010496. eCollection 2020. Sarcoma. 2020. PMID: 33005093 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the Actin Machinery in Programmed Cell Death.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 9;8:634849. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.634849. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33634110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Forecast of actin-binding proteins as the oncotarget in osteosarcoma - a review of mechanism, diagnosis and therapy.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Mar 20;11:1553-1561. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S159894. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 29593421 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shi X, Xu M, Liu YX, et al Preliminary report of a randomized controlled multicenter study of first‐line chemotherapy regimen combined with angiogenesis inhibitor for osteosarcoma of the extremities. Zhonghua Gu Ke Za Zhi, 2012, 32: 1027–1031 (in Chinese).
-
- Lin N, Ye ZM, Li P, Li WX, Tao HM, Yang DS, et al The diuleal features and prognostic factors of osteosarcoma in adult. Zhonghua Gu Ke Za Zhi, 2009, 29: 717–722 (in Chinese).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

