The Relationship Between Psychological Distress, Negative Cognitions, and Expectancies on Problem Drinking: Exploring a Growing Problem Among University Students
- PMID: 26311191
- PMCID: PMC4740224
- DOI: 10.1177/0145445515601793
The Relationship Between Psychological Distress, Negative Cognitions, and Expectancies on Problem Drinking: Exploring a Growing Problem Among University Students
Abstract
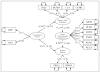
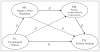
Few studies have sought to understand the concurrent relationship between cognitive and affective processes on alcohol use and negative alcohol-related consequences, despite both being identified as predictive risk factors in the college population. More research is needed to understand the relationships between identified factors of problem drinking among this at-risk population. The purpose of this study was to test if the relationship between psychological distress and problem drinking among university students (N = 284; M-age = 19.77) was mediated by negative affect regulation strategies and positive alcohol-related expectancies. Two latent mediation models of problem drinking were tested using structural equation modeling (SEM). The parsimonious three-path mediated latent model was supported by the data, as evidenced by several model fit indices. Furthermore, the alternate saturated model provided similar fit to the data, but contained several direct relationships that were not statistically significant. The relationship between psychological distress and problem drinking was mediated by an extended contributory chain, including negative affect regulation and positive alcohol-related expectancies. Implications for prevention and treatment, as well as future directions, are discussed.
Keywords: affect regulation; alcohol; alcohol-related expectancies; anxiety; depression; problem drinking.
© The Author(s) 2015.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alcohol expectancies and drinking motives in college drinkers: Mediating effects on the relationship between generalized anxiety and heavy drinking in negative-affect situations.Addict Behav. 2009 Jun-Jul;34(6-7):505-13. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2009.01.003. Epub 2009 Jan 31. Addict Behav. 2009. PMID: 19249161
-
Alcohol expectancies and context-specific drinking behaviors among female college athletes.Behav Ther. 2008 Jun;39(2):162-70. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2007.06.002. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Behav Ther. 2008. PMID: 18502249
-
Protective behavioral strategies mediate problem-focused coping and alcohol use in college students.Addict Behav. 2014 Jun;39(6):1033-7. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2014.02.006. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Addict Behav. 2014. PMID: 24629479
-
Magnitude of the problem of drinking alcohol on college campuses, commentary on "Structuring a college alcohol prevention program on the low level of response to alcohol model: a pilot model".Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012 Jul;36(7):1126-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2012.01828.x. Epub 2012 May 16. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012. PMID: 22591168 Review.
-
College students and problematic drinking: a review of the literature.Clin Psychol Rev. 2003 Oct;23(5):719-59. doi: 10.1016/s0272-7358(03)00071-0. Clin Psychol Rev. 2003. PMID: 12971907 Review.
Cited by
-
Phenome-Wide Association Study for Alcohol and Nicotine Risk Alleles in 26394 Women.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016 Oct;41(11):2688-96. doi: 10.1038/npp.2016.72. Epub 2016 May 17. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016. PMID: 27187070 Free PMC article.
-
Difficulties with positive, but not negative, emotion regulation moderate the association between positive alcohol expectancies and alcohol use in college students.Addict Behav Rep. 2025 Jan 7;21:100583. doi: 10.1016/j.abrep.2025.100583. eCollection 2025 Jun. Addict Behav Rep. 2025. PMID: 39866222 Free PMC article.
-
Adolescent Alcohol and Stress Exposure Rewires Key Cortical Neurocircuitry.Front Neurosci. 2022 May 17;16:896880. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.896880. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35655755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armeli S, Todd M, Mohr C. A daily process approach to individual differences in stress-related alcohol use. Journal of Personality. 2005;73:1657–1686. - PubMed
-
- Augustine AA, Larsen RJ. Personality, affect, and affect regulation. In: Mikulincer M, Saver PR, Cooper ML, Larsen RJ, editors. APA handbook of personality and social psychology, Volume 4: Personality processes and individual differences. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; 2015. pp. 147–165.
-
- Baker TB, Piper ME, McCarthy DE, Majeskie MR, Fiore MC. Addiction motivation reformulated: An affective processing model of negative reinforcement. Psychological Review. 2004;111:33–51. - PubMed
-
- Bandura A. Principles of behavior modification. New York, NY: Hold, Rinehart & Winston; 1969.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

