A subset of ocular adnexal marginal zone lymphomas may arise in association with IgG4-related disease
- PMID: 26311608
- PMCID: PMC4550912
- DOI: 10.1038/srep13539
A subset of ocular adnexal marginal zone lymphomas may arise in association with IgG4-related disease
Abstract
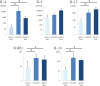
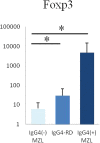
We previously suggested a relationship between ocular immunoglobulin (Ig)G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) and marginal zone lymphomas (MZLs). However, the cytokine background associated with these disorders and whether it differs between ocular adnexal MZLs with (IgG4-associated MZL) and without (IgG4-negative MZL) numerous IgG4(+) plasma cells are unknown. In this study, we identified the mRNA expression pattern of Th2 and regulatory T-cell (Treg) cytokines in IgG4-RD and in IgG4-associated MZL and IgG4-negative MZL using real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis. Ocular IgG4-RD and IgG4-associated MZL exhibited significantly higher expression ratios of interleukin (IL)-4/β-actin, IL-10/β-actin, IL-13/β-actin, transforming growth factor (TGF) β1/β-actin, and FOXP3/β-actin than did IgG4-negative MZL (p < 0.05). This finding further supports our prior observations that a significant subset of ocular MZLs arises in the setting of IgG4-RD. Furthermore, the presence of a different inflammatory background in IgG4-negative MZLs suggests that IgG4-associated MZLs may have a different pathogenesis.
Figures
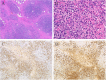
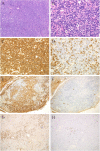
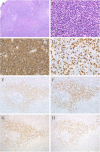
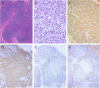
References
-
- Sato Y. et al. Ocular adnexal IgG4-related disease has uniform clinicopathology. Pathol. Int. 58, 465–70 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Sato Y. et al. Ocular adnexal IgG4-producing mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma mimicking IgG4-related disease. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 52, 51–5 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Sato Y. et al. IgG4-related disease: historical overview and pathology of hematological disorders. Pathol. Int. 60, 247–58 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Masaki Y., Kurose N. & Umehara H. IgG4-related disease: a novel lymphoproliferative disorder discovered and established in Japan in the 21st century. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 51, 13–20 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Stone J. H. et al. IgG4-related systemic disease and lymphoplasmacytic aortitis. Arthritis Rheum. 60, 3139–45 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

