Characterization of the Interaction between the Matrix Protein of Vesicular Stomatitis Virus and the Immunoproteasome Subunit LMP2
- PMID: 26311888
- PMCID: PMC4621137
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01753-15
Characterization of the Interaction between the Matrix Protein of Vesicular Stomatitis Virus and the Immunoproteasome Subunit LMP2
Abstract
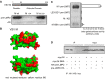
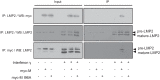
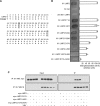
The matrix protein (M) of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) is involved in virus assembly, budding, gene regulation, and cellular pathogenesis. Using a yeast two-hybrid system, the M globular domain was shown to interact with LMP2, a catalytic subunit of the immunoproteasome (which replaces the standard proteasome catalytic subunit PSMB6). The interaction was validated by coimmunoprecipitation of M and LMP2 in VSV-infected cells. The sites of interaction were characterized. A single mutation of M (I96A) which significantly impairs the interaction between M and LMP2 was identified. We also show that M preferentially binds to the inactive precursor of LMP2 (bearing an N-terminal propeptide which is cleaved upon LMP2 maturation). Furthermore, taking advantage of a sequence alignment between LMP2 and its proteasome homolog, PSMB6 (which does not bind to M), we identified a mutation (L45R) in the S1 pocket where the protein substrate binds prior to cleavage and a second one (D17A) of a conserved residue essential for the catalytic activity, resulting in a reduction of the level of binding to M. The combination of both mutations abolishes the interaction. Taken together, our data indicate that M binds to LMP2 before its incorporation into the immunoproteasome. As the immunoproteasome promotes the generation of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-compatible peptides, a feature which favors the recognition and the elimination of infected cells by CD8 T cells, we suggest that M, by interfering with the immunoproteasome assembly, has evolved a mechanism that allows infected cells to escape detection and elimination by the immune system.
Importance: The immunoproteasome promotes the generation of MHC class I-compatible peptides, a feature which favors the recognition and the elimination of infected cells by CD8 T cells. Here, we report on the association of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) matrix protein (M) with LMP2, one of the immunoproteasome-specific catalytic subunits. M preferentially binds to the LMP2 inactive precursor. The M-binding site on LMP2 is facing inwards in the immunoproteasome and is therefore not accessible to M after its assembly. Hence, M binds to LMP2 before its incorporation into the immunoproteasome. We suggest that VSV M, by interfering with the immunoproteasome assembly, has evolved a mechanism that allows infected cells to escape detection and elimination by the immune system. Modulating this M-induced immunoproteasome impairment might be relevant in order to optimize VSV for oncolytic virotherapy.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus binds dynamin for efficient viral assembly.J Virol. 2010 Dec;84(24):12609-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01400-10. Epub 2010 Oct 13. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20943988 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking the Fate of Genetically Distinct Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Matrix Proteins Highlights the Role for Late Domains in Assembly.J Virol. 2015 Dec;89(23):11750-60. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01371-15. Epub 2015 Sep 2. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26339059 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix protein of VSV New Jersey serotype containing methionine to arginine substitutions at positions 48 and 51 allows near-normal host cell gene expression.Virology. 2007 Jan 5;357(1):41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.07.022. Epub 2006 Sep 7. Virology. 2007. PMID: 16962155
-
The immunoproteasome and viral infection: a complex regulator of inflammation.Front Microbiol. 2015 Jan 29;6:21. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00021. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25688236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CANDLE Syndrome As a Paradigm of Proteasome-Related Autoinflammation.Front Immunol. 2017 Aug 9;8:927. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00927. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28848544 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Components and Architecture of the Rhabdovirus Ribonucleoprotein Complex.Viruses. 2020 Aug 29;12(9):959. doi: 10.3390/v12090959. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32872471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PSMB5 plays a dual role in cancer development and immunosuppression.Am J Cancer Res. 2017 Nov 1;7(11):2103-2120. eCollection 2017. Am J Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29218236 Free PMC article.
-
EIF3i affects vesicular stomatitis virus growth by interacting with matrix protein.Vet Microbiol. 2017 Dec;212:59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.10.021. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Vet Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29173589 Free PMC article.
-
The Immunoproteasome Is Expressed but Dispensable for a Leukemia Infected Cell Vaccine.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Aug 5;13(8):835. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13080835. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40872920 Free PMC article.
-
M51R and Delta-M51 matrix protein of the vesicular stomatitis virus induce apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Jun;46(3):3371-3379. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-04799-3. Epub 2019 Apr 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31006094
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

