Environmental influences on the Indo-Pacific octocoral Isis hippuris Linnaeus 1758 (Alcyonacea: Isididae): genetic fixation or phenotypic plasticity?
- PMID: 26312170
- PMCID: PMC4548502
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.1128
Environmental influences on the Indo-Pacific octocoral Isis hippuris Linnaeus 1758 (Alcyonacea: Isididae): genetic fixation or phenotypic plasticity?
Abstract
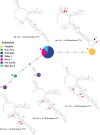
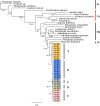
As conspicuous modular components of benthic marine habitats, gorgonian (sea fan) octocorals have perplexed taxonomists for centuries through their shear diversity, particularly throughout the Indo-Pacific. Phenotypic incongruence within and between seemingly unitary lineages across contrasting environments can provide the raw material to investigate processes of disruptive selection. Two distinct phenotypes of the Isidid Isis hippurisLinnaeus, 1758 partition between differing reef environments: long-branched bushy colonies on degraded reefs, and short-branched multi/planar colonies on healthy reefs within the Wakatobi Marine National Park (WMNP), Indonesia. Multivariate analyses reveal phenotypic traits between morphotypes were likely integrated primarily at the colony level with increased polyp density and consistently smaller sclerite dimensions at the degraded site. Sediment load and turbidity, hence light availability, primarily influenced phenotypic differences between the two sites. This distinct morphological dissimilarity between the two sites is a reliable indicator of reef health; selection primarily acting on colony morphology, porosity through branching structure, as well as sclerite diversity and size. ITS2 sequence and predicted RNA secondary structure further revealed intraspecific variation between I. hippuris morphotypes relative to such environments (ΦST = 0.7683, P < 0.001). This evidence suggests-but does not confirm-that I. hippuris morphotypes within the WMNP are two separate species; however, to what extent and taxonomic assignment requires further investigation across its full geographic distribution. Incongruence between colonies present in the WMNP with tenuously described Isis alternatives (Isis reticulataNutting, 1910, Isis minorbrachyblastaZou, Huang & Wang, 1991), questions the validity of such assignments. Furthermore, phylogenetic analyses confirm early taxonomic suggestion that the characteristic jointed axis of the Isididae is in fact a convergent trait. Thus the polyphyletic nature of the Isididae lies in its type species I. hippuris, being unrelated to the rest of its family members.
Keywords: Gorgonian coral; ITS2; Indonesia; Isididae; Isis hippuris; Morphology; Wakatobi Marine National Park (WMNP).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests. Xavier Pochon is an employee of the Cawthron Institute.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Phenotypic plasticity and morphological integration in a marine modular invertebrate.BMC Evol Biol. 2007 Jul 24;7:122. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-7-122. BMC Evol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17650324 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic plasticity or speciation? A case from a clonal marine organism.BMC Evol Biol. 2008 Feb 13;8:47. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-8-47. BMC Evol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18271961 Free PMC article.
-
Toward a revision of the bamboo corals: Part 3, deconstructing the Family Isididae.Zootaxa. 2021 Sep 30;5047(3):247-272. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.5047.3.2. Zootaxa. 2021. PMID: 34810847
-
Environmental impacts of dredging and other sediment disturbances on corals: a review.Mar Pollut Bull. 2012 Sep;64(9):1737-65. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.05.008. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Mar Pollut Bull. 2012. PMID: 22682583 Review.
-
Biology and ecology of the hydrocoral millepora on coral reefs.Adv Mar Biol. 2006;50:1-55. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2881(05)50001-4. Adv Mar Biol. 2006. PMID: 16782450 Review.
Cited by
-
The Octocoral Trait Database: a global database of trait information for octocoral species.Sci Data. 2025 Jan 15;12(1):82. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-04307-8. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 39814778 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental filtering and neutral processes shape octocoral community assembly in the deep sea.Oecologia. 2017 Jan;183(1):221-236. doi: 10.1007/s00442-016-3765-4. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Oecologia. 2017. PMID: 27826800
-
A next generation approach to species delimitation reveals the role of hybridization in a cryptic species complex of corals.BMC Evol Biol. 2019 Jun 6;19(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12862-019-1427-y. BMC Evol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31170912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abràmoff M, Magalhaes PJ, Ram SJ. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics International. 2004;11:36–42.
-
- Alderslade P. Revisionary systematics in the gorgonian family Isididae, with descriptions of numerous taxa (Coelenterata: Octocorallia) Perth: Western Australian Museum; 1998. pp. 1–359. (Records of the Western Australian Museum, Supplement No. 55).
-
- Anderson MJ. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Australian Ecology. 2001;26:32–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-9993.2001.01070.pp.x. - DOI
-
- Anderson MJ. Auckland: Department of Statistics, University of Auckland, New ZealandDISTLMforward: a FORTRAN computer program to calculate a distance based multivariate analysis for a linear model using forward selection. 2003
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

