Protective effect of Emblica-officinalis in arsenic induced biochemical alteration and inflammation in mice
- PMID: 26312203
- PMCID: PMC4545902
- DOI: 10.1186/s40064-015-1227-9
Protective effect of Emblica-officinalis in arsenic induced biochemical alteration and inflammation in mice
Abstract
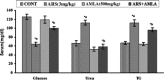
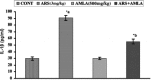
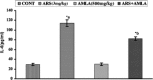
Exposure to arsenic in individuals has been found to be associated with immune related problems. In earlier studies, we have demonstrated that amla protects against arsenic induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in thymus and spleen of mice. In continuation to that the present study has therefore been focused to investigate the protective efficacy of amla in arsenic induced inflammation and immunotoxicity in mice. The results showed that arsenic treatment significantly increased serum urea levels (69 %), glucose levels (48 %) and triglyceride levels (66 %) as compared to controls. Mice exposed to arsenic exhibited significant increased in TNF-α (4.3-fold), serum Interleukin-1 beta (threefold), Interleukin-6 (3.8-fold) as compared to controls. Arsenic exposure increased the relative frequency of CD8+ (Tc) cells sub-population (18.9 %) and decreased CD4+ (Th) cells (2.6 %). Arsenic exposure also significantly decreased T (CD3) and B (CD19) cells (21.1 %) as compared to controls. Simultaneously treatment with arsenic and amla significantly inhibited serum urea levels (47 %), glucose levels (50 %) and triglyceride levels (14 %). It also significantly decreased the TNF-α (1.1-fold), levels of IL-1β (1.6-fold), levels of Interleukin-6 (1.3-fold) in serum as compared to those treated with arsenic alone. Simultaneously treatment with arsenic and amla restored the alterations in CD8+ and CD4+ cells and also recovered the damages in B and T sub cells population. Results of the present study clearly indicate that arsenic induced immunotoxicity linked with inflammation has been significantly protected through simultaneous treatment with arsenic and amla that was due to anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity of amla.
Keywords: Amla; Arsenic; Immunotoxicity; Inflammation; Mice.
Figures


References
-
- Anilkumar KR, Nagaraj NS, Santhanam K. Reduction of hexachlorocyclohexane-induced oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in rat liver by Emblica officinalis Gaertn. Indian J Exp Biol. 2007;45:450–454. - PubMed
-
- Ballentine-Burfor DD. Determination of metals. Methods Enzymol. 1957;3:1002–1035. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(57)03493-X. - DOI
-
- Banerjee N, Nandy S, Kearns JK, Bandyopadhyay AK, Das JK, Majumdez P, Basu S, Banerjee S, Sau TJ, States JC, Giri AK. Polymorphisms in the TNF-and alpha; and IL10-gene promoters and risk of arsenic-induced skin lesions and other non-dermatological health effects. Toxicol Sci. 2011;121(1):132–139. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr046. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

