A new semantic list learning task to probe functioning of the Papez circuit
- PMID: 26313512
- PMCID: PMC5065919
- DOI: 10.1080/13803395.2015.1052732
A new semantic list learning task to probe functioning of the Papez circuit
Abstract
Introduction: List learning tasks are powerful clinical tools for studying memory, yet have been relatively underutilized within the functional imaging literature. This limits understanding of regions such as the Papez circuit that support memory performance in healthy, nondemented adults.
Method: The current study characterized list learning performance in 40 adults who completed a semantic list learning task (SLLT) with a Brown-Peterson manipulation during functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Cued recall with semantic cues and recognition memory were assessed after imaging. Internal reliability, convergent, and discriminant validity were evaluated.
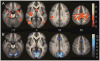
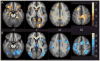
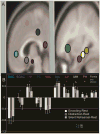
Results: Subjects averaged 38% accuracy in recall (62% for recognition), with primacy but no recency effects observed. Validity and reliability were demonstrated by showing that the SLLT was correlated with the California Verbal Learning Test (CVLT), but not with executive functioning tests, and by high intraclass correlation coefficient across lists for recall (.91). fMRI measurements during encoding (vs. silent rehearsal) revealed significant activation in bilateral hippocampus, parahippocampus, and bilateral anterior and posterior cingulate cortex. Post hoc analyses showed increased activation in anterior and middle hippocampus, subgenual cingulate, and mammillary bodies specific to encoding. In addition, increasing age was positively associated with increased activation in a diffuse network, particularly frontal cortex and specific Papez regions for correctly recalled words. Gender differences were specific to left inferior and superior frontal cortex.
Conclusions: This is a clinically relevant list learning task that can be used in studies of groups for which the Papez circuit is damaged or disrupted, in mixed or crossover studies at imaging and clinical sites.
Keywords: Functional magnetic resonance imaging; Hippocampus; Imaging; List learning; Memory; Papez circuit.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Decreased Fronto-Limbic Activation and Disrupted Semantic-Cued List Learning in Major Depressive Disorder.J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2016 Apr;22(4):412-25. doi: 10.1017/S1355617716000023. Epub 2016 Feb 2. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2016. PMID: 26831638 Free PMC article.
-
Neural correlates of episodic and semantic memory retrieval in borderline personality disorder: an fMRI study.Psychiatry Res. 2009 Feb 28;171(2):94-105. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2008.02.006. Epub 2009 Jan 26. Psychiatry Res. 2009. PMID: 19176280
-
Age differences in hippocampus-cortex connectivity during true and false memory retrieval.J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2013 Nov;19(10):1031-41. doi: 10.1017/S1355617713001069. Epub 2013 Sep 23. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2013. PMID: 24060006
-
Age differences in the neural correlates of novelty processing: The effects of item-relatedness.Brain Res. 2015 Jul 1;1612:2-15. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Aug 19. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25149192 Review.
-
A modified neural circuit framework for semantic memory retrieval with implications for circuit modulation to treat verbal retrieval deficits.Brain Behav. 2024 May;14(5):e3490. doi: 10.1002/brb3.3490. Brain Behav. 2024. PMID: 38680077 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Decreased Fronto-Limbic Activation and Disrupted Semantic-Cued List Learning in Major Depressive Disorder.J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2016 Apr;22(4):412-25. doi: 10.1017/S1355617716000023. Epub 2016 Feb 2. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2016. PMID: 26831638 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of Attrition in Longitudinal Neuroimaging Research: Inhibitory Control, Head Movement, and Resting-State Functional Connectivity.Brain Connect. 2018 Nov;8(9):527-536. doi: 10.1089/brain.2018.0619. Brain Connect. 2018. PMID: 30411975 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-scan cortisol is differentially associated with enhanced connectivity to the cognitive control network in young adults with a history of depression.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019 Jun;104:219-227. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2019.03.007. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019. PMID: 30889471 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive outcomes are differentially associated with depression severity trajectories during psychotherapy treatment for late life major depressive disorder.Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2022 Aug;37(8):10.1002/gps.5779. doi: 10.1002/gps.5779. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35822633 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability, Convergent Validity and Time Invariance of Default Mode Network Deviations in Early Adult Major Depressive Disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2018 Jun 8;9:244. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00244. eCollection 2018. Front Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29937738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreano JM, Cahill L. Sex influences on the neurobiology of learning and memory. Learning and Memory. 2009;16:248–266. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson RC, Shiffrin RM. Human memory: A proposed system and its control processes. In: Spence KW, Spence JT, editors. The psychology of learning and motivation. New York: Academic Press; 1968. pp. 89–195.
-
- Baddeley A, Bueno O, Cahill L, Fuster JM, Izquierdo I, McGaugh JL, et al. The brain decade in debate: I. Neurobiology of learning and memory. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research. 2000;33:993–1002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
