Squamous Cell Carcinoma Xenografts: Use of VEGFR2-targeted Microbubbles for Combined Functional and Molecular US to Monitor Antiangiogenic Therapy Effects
- PMID: 26313618
- PMCID: PMC5410993
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2015142899
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Xenografts: Use of VEGFR2-targeted Microbubbles for Combined Functional and Molecular US to Monitor Antiangiogenic Therapy Effects
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the ability of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor type 2 (VEGFR2)-targeted and nontargeted ultrasonography (US) to depict antiangiogenic therapy effects and to investigate whether first-pass kinetics obtained with VEGFR2-targeted microbubbles provide independent data about tumor vascularization.
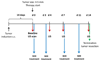
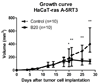
Materials and methods: Governmental approval was obtained for animal experiments. Vascularization in response to anti-vascular endothelial growth factor receptor or vehicle-control treatment (10 per group) in HaCaT-ras A-5RT3 xenografts was longitudinally assessed in mice by means of first-pass kinetics of nontargeted microbubbles (BR1, BR38; Bracco, Geneva, Switzerland) and VEGFR2-targeted microbubbles (BR55, Bracco) before and 4, 7, and 14 days after therapy. VEGFR2 expression was determined 8 minutes after BR55 injection with destruction-replenishment analysis. US data were validated with immunohistochemistry. Significant differences were evaluated with the Mann-Whitney test.
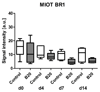
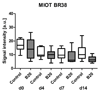
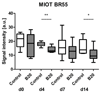
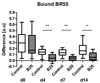
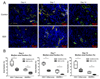
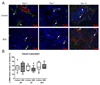
Results: First-pass analysis with BR1, BR38, and BR55 showed similar tendencies toward decreasing vascularization, with a stronger decrease in tumors treated with anti-VEGF antibody. The median signal intensity (in arbitrary units [au]) of anti-VEGF antibody-treated versus control tumors at day 14 was as follows: BR1, 5.2 au (interquartile range [IQR], 3.2 au) vs 11.3 au (IQR, 10.0 au), respectively; BR38, 6.2 au (IQR, 3.5) vs 10.0 au (IQR, 7.8); and BR55, 9.5 au (IQR, 6.0 au) vs 13.8 au (IQR, 9.8) (P = .0230). VEGFR2 assessment with BR55 demonstrated significant differences between both groups throughout the therapy period (median signal intensity of anti-VEGF antibody-treated vs control tumors: 0.04 au [IQR, 0.1 au] vs 0.14 au [IQR, 0.08 au], respectively, at day 4, P = .0058; 0.04 au [IQR, 0.06 au] vs 0.13 au [IQR, 0.09 au] at day 7, P = .0058; and 0.06 au [IQR, 0.11 au] vs 0.16 au [IQR, 0.15 au] at day 14, P = .0247). Immunohistochemistry confirmed the lower microvessel density and VEGFR2-positive area fraction in tumors treated with anti-VEGF antibody.
Conclusion: Antiangiogenic therapy effects were detected earlier and more distinctly with VEGFR2-targeted US than with functional US. First-pass analyses with BR55, BR38, and BR1 revealed similar results, with a decrease in vascularization during therapy. Functional data showed that BR55 is not strongly affected by early binding of the microbubbles to VEGFR2. Thus, functional and molecular imaging of angiogenesis can be performed with BR55 within one examination.
© RSNA, 2015.
Figures
References
-
- Rossi D, Zlotnik A. The biology of chemokines and their receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:217–242. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature. 2000;407(6801):249–257. - PubMed
-
- Romagnani P, Lasagni L, Annunziato F, Serio M, Romagnani S. CXC chemokines: the regulatory link between inflammation and angiogenesis. Trends Immunol. 2004;25(4):201–209. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

