α-Solanine induces ROS-mediated autophagy through activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and inhibition of Akt/mTOR pathway
- PMID: 26313911
- PMCID: PMC4558510
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2015.219
α-Solanine induces ROS-mediated autophagy through activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and inhibition of Akt/mTOR pathway
Abstract
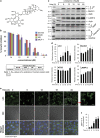
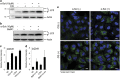
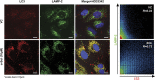
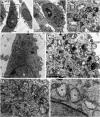
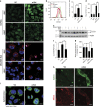
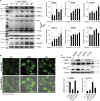
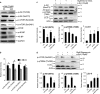
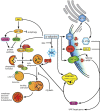
α-Solanine is a glycoalkaloid found in species of the nightshade family including potato. It was primarily reported to have toxic effects in humans. However, there is a growing body of literature demonstrating in vitro and in vivo anticancer activity of α-solanine. Most of these studies have shown activation of apoptosis as the underlying mechanism in antitumor activity of α-solanine. In this study, we report α-solanine as a potential inducer of autophagy, which may act synergistically or in parallel with apoptosis to exert its cytotoxic effect. Induction of autophagy was demonstrated by several assays including electron microscopy, immunoblotting of autophagy markers and immunofluorescence for LC3 (microtubule-associated protein 1 (MAP1) light chain-3) puncta. α-Solanine-induced autophagic flux was demonstrated by additionally enhanced--turnover of LC3-II and--accumulation of LC3-specific puncta after co-incubation of cells with either of the autophagolysosome inhibitors--chloroquine and--bafilomycin A1. We also demonstrated α-solanine-induced oxidative damage in regulating autophagy where pre-incubation of cells with reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger resulted in suppression of CM-H2DCFDA (5 (and 6)-chloromethyl-2',7'-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate acetyl ester) fluorescence as well as decrease in LC3-II turnover. α-Solanine treatment caused an increase in the expression of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress proteins (BiP, activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6), X-box-binding protein 1, PERK, inositol-requiring transmembrane kinase/endonuclease 1, ATF4 and CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP)-homologous protein) suggesting activation of unfolded protein response pathway. Moreover, we found downregulation of phosphorylated Akt (Thr308 and Ser473), mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR; Ser2448 and Ser2481) and 4E-BP1 (Thr37/46) by α-solanine implying suppression of the Akt/mTOR pathway. Collectively, our results signify that α-solanine induces autophagy to exert anti-proliferative activity by triggering ER stress and inhibiting Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The kinase PERK and the transcription factor ATF4 play distinct and essential roles in autophagy resulting from tunicamycin-induced ER stress.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 17;294(20):8197-8217. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002829. Epub 2019 Mar 29. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30926605 Free PMC article.
-
The GST-BHMT assay reveals a distinct mechanism underlying proteasome inhibition-induced macroautophagy in mammalian cells.Autophagy. 2015;11(5):812-32. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1034402. Autophagy. 2015. PMID: 25984893 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic trioxide induces unfolded protein response in vascular endothelial cells.Arch Toxicol. 2014 Feb;88(2):213-26. doi: 10.1007/s00204-013-1101-x. Epub 2013 Jul 27. Arch Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 23892647
-
Molecular signal networks and regulating mechanisms of the unfolded protein response.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017 Jan.;18(1):1-14. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1600043. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017. PMID: 28070992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Basis of Human Diseases and Targeted Therapy Based on Small-Molecule Inhibitors of ER Stress-Induced Signaling Pathways.Curr Mol Med. 2017;17(2):118-132. doi: 10.2174/1566524017666170306122643. Curr Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28266275 Review.
Cited by
-
Updated aspects of alpha-Solanine as a potential anticancer agent: Mechanistic insights and future directions.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Aug 29;12(10):7088-7107. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4221. eCollection 2024 Oct. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39479710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
α-Solanine Inhibits Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration, and Induces Apoptosis in Human Choriocarcinoma JEG-3 Cells In Vitro and In Vivo.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Mar 13;13(3):210. doi: 10.3390/toxins13030210. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805658 Free PMC article.
-
Tinospora sinensis (Lour.) Merr alkaloid rich extract induces colon cancer cell death via ROS mediated, mTOR dependent apoptosis pathway: "an in-vitro study".BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Feb 3;23(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03849-5. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 36737760 Free PMC article.
-
Dysfunction of various organelles provokes multiple cell death after quantum dot exposure.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 May 7;13:2729-2742. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S157135. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29765216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Combination of Lead and Bacillus coagulans R11 Increased the Concentration of Alpha-Solanine in the Cecum of Laying Hens and the Pathogens Abundance Decreased.Front Microbiol. 2020 Oct 21;11:585197. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.585197. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33193232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Korpan YI, Nazarenko EA, Skryshevskaya, Martelet C, Jaffrezic-Renault N, El'skaya AV. Potato glycoalkaloids: true safety or false sense of security. Trends Biotechnol. 2004;22:147–151. - PubMed
-
- Maga JA. Potato glycoalkaloids. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1980;12:371–405. - PubMed
-
- Friedman M, McDonald GM, Filadelfi-Keszi M. Potato glycoalkaloids: chemistry, analysis, safety, and plant physiology. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 1997;16:55–132.
-
- McMillan M, Thompson JC. An outbreak of suspected solanine poisoning in schoolboys: examinations of criteria of solanine poisoning. Q J Med. 1979;48:227–243. - PubMed
-
- Rayburn JR, Bantle JA, Friedman M. Role of carbohydrate side chains of potato glycoalkaloids in developmental toxicity. J Agr Food Chem. 1994;42:1511–1515.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

