Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 protects against acute myeloid leukemia by suppressing the myeloproliferative leukemia virus oncogene
- PMID: 26314963
- PMCID: PMC4695004
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4748
Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 protects against acute myeloid leukemia by suppressing the myeloproliferative leukemia virus oncogene
Abstract
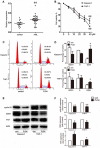
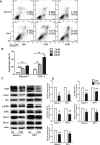
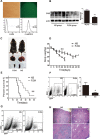
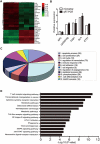
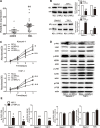
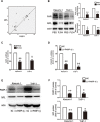
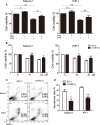
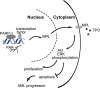
An abnormal expression of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) has been described in many tumors. PARP-1 promotes tumorigenesis and cancer progression by acting on different molecular pathways. PARP-1 inhibitors can be used with radiotherapy or chemotherapy to enhance the susceptibility of tumor cells to the treatment. However, the specific mechanism of PARP-1 in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remains unknown. Our study showed that expression of PARP-1 was upregulated in AML patients. PARP-1 inhibition slowed AML cell proliferation, arrested the cell cycle, induced apoptosis in vitro and improved AML prognosis in vivo. Mechanistically, microarray assay of AML cells with loss of PARP-1 function revealed that the myeloproliferative leukemia virus oncogene (MPL) was significantly downregulated. In human AML samples, MPL expression was increased, and gain-of-function and loss-of-function analysis demonstrated that MPL promoted cell growth. Moreover, PARP-1 and MPL expression were positively correlated in AML samples, and their overexpression was associated with an unfavorable prognosis. Furthermore, PARP-1 and MPL consistently acted on Akt and ERK1/2 pathways, and the anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic function observed with PARP-1 inhibition were reversed in part via MPL activation upon thrombopoietin stimulation or gene overexpression. These data highlight the important function of PARP-1 in the progression of AML, which suggest PARP-1 as a potential target for AML treatment.
Keywords: MPL; PARP-1; acute myeloid leukemia; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Daver N, Cortes J. Molecular targeted therapy in acute myeloid leukemia. Hematology. 2012;17:S59–62. - PubMed
-
- Schreiber V, Dantzer F, Ame JC, de Murcia G. Poly(ADP-ribose): novel functions for an old molecule. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:517–528. - PubMed
-
- Kraus WL, Hottiger MO. PARP-1 and gene regulation: progress and puzzles. Mol Aspects Med. 2013;34:1109–1123. - PubMed
-
- Pleschke JM, Kleczkowska HE, Strohm M, Althaus FR. Poly(ADP-ribose) binds to specific domains in DNA damage checkpoint proteins. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:40974–40980. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

