MiR-23a sensitizes nasopharyngeal carcinoma to irradiation by targeting IL-8/Stat3 pathway
- PMID: 26314966
- PMCID: PMC4695064
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5117
MiR-23a sensitizes nasopharyngeal carcinoma to irradiation by targeting IL-8/Stat3 pathway
Abstract
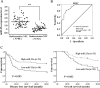
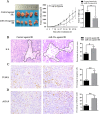
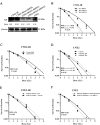
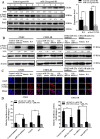
Radioresistance poses a major challenge in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) treatment, but little is known about how miRNA regulates this phenomenon. In this study, we investigated the function and mechanism of miR-23a in NPC radioresistance, one of downregulated miRNAs in the radioresistant NPC cells identified by our previous microarray analysis. We observed that miR-23a was frequently downregulated in the radioresistant NPC tissues, and its decrement correlated with NPC radioresistance and poor patient survival, and was an independent predictor for reduced patient survival. In vitro radioresponse assays showed that restoration of miR-23a expression markedly increased NPC cell radiosensitivity. In a mouse model, therapeutic administration of miR-23a agomir dramatically sensitized NPC xenografts to irradiation. Mechanistically, we found that reduced miR-23a promoted NPC cell radioresistance by activating IL-8/Stat3 signaling. Moreover, the levels of IL-8 and phospho-Stat3 were increased in the radioresistance NPC tissues, and negatively associated with miR-23a level. Our data demonstrate that miR-23a is a critical determinant of NPC radioresponse and prognostic predictor for NPC patients, and its decrement enhances NPC radioresistance through activating IL-8/Stat3 signaling, highlighting the therapeutic potential of miR-23a/IL-8/Stat3 signaling axis in NPC radiosensitization.
Keywords: IL-8; Stat3; miR-23a; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; radioresistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lo KW, To KF, Huang DP. Focus on nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2004;5:423–428. - PubMed
-
- Kristensen CA, Kjaer-Kristoffersen F, Sapru W, Berthelsen AK, Loft A, Specht L. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Treatment planning with IMRT and 3D conformal radiotherapy. Acta Oncologica. 2007;46:214–220. - PubMed
-
- Lee AW, Poon Y, Foo W, Law SC, Cheung FK, Chan DK, Tung SY, Thaw M, Ho JH. Retrospective analysis of 5037 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated during 1976-1985: overall survival and patterns of failure. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992;23:261–270. - PubMed
-
- Garzon R, Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 2009;60:167–179. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhry MA. Radiation-induced microRNA: Discovery, functional analysis, and cancer radiotherapy. J Cell Biochem. 2014;115:436–449. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

