Promotion of Inflammatory Arthritis by Interferon Regulatory Factor 5 in a Mouse Model
- PMID: 26315890
- PMCID: PMC4661118
- DOI: 10.1002/art.39321
Promotion of Inflammatory Arthritis by Interferon Regulatory Factor 5 in a Mouse Model
Abstract
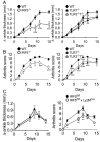
Objective: Polymorphisms in the transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) are associated with an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This study was undertaken to determine the role of IRF5 in a mouse model of arthritis development.
Methods: K/BxN serum-transfer arthritis was induced in mice deficient in IRF5, or lacking IRF5 only in myeloid cells, and arthritis severity was evaluated. K/BxN arthritis was also induced in mice deficient in TRIF, Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), TLR3, TLR4, and TLR7 to determine the pathways through which IRF5 might promote arthritis. In vitro studies were performed to determine the role of IRF5 in interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor and TLR signaling.
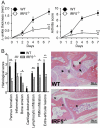
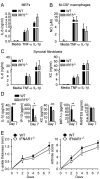
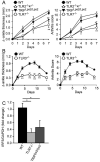
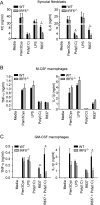
Results: Arthritis severity was reduced in IRF5-deficient, TRIF-deficient, TLR3-deficient, and TLR7-deficient mice. The expression of multiple genes regulating neutrophil recruitment or function and bioactive IL-1β formation was reduced in the joints during active arthritis in IRF5-deficient mice. In vitro studies showed that TLR7 and the TRIF-dependent TLR3 pathway induce proinflammatory cytokine production in disease-relevant cell types in an IRF5-dependent manner.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that IRF5 contributes to disease pathogenesis in inflammatory arthritis. This is likely due at least in part to the role of IRF5 in mediating proinflammatory cytokine production downstream of TLR7 and TLR3. Since TLR7 and TLR3 are both RNA-sensing TLRs, this suggests that endogenous RNA ligands present in the inflamed joint promote arthritis development. These findings may be relevant to human RA, since RNA capable of activating TLR7 and TLR3 is present in synovial fluid and TLR7 and TLR3 are up-regulated in the joints of RA patients.
© 2015, American College of Rheumatology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Autoimmunity. IRF5 mediates joint inflammation.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015 Oct;11(10):562. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2015.127. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26369611 No abstract available.
References
-
- McInnes IB, O'Dell JR. State-of-the-art: rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:1898–1906. - PubMed
-
- Dieguez-Gonzalez R, Calaza M, Perez-Pampin E, de la Serna AR, Fernandez-Gutierrez B, Castaneda S, et al. Association of interferon regulatory factor 5 haplotypes, similar to that found in systemic lupus erythematosus, in a large subgroup of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:1264–1274. - PubMed
-
- Monach P, Hattori K, Huang H, Hyatt E, Morse J, Nguyen L, et al. The K/BxN mouse model of inflammatory arthritis: theory and practice. Methods Mol Med. 2007;136:269–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K01-AR-060169/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007053/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01-AR-055965/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-054796/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR055965/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01-AR-050256/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL108795/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR060857/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR051089/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-050250/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01-HL-108795/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM107000/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-055952/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK095058/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR050250/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR054796/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AR050256/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AR060169/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-051089/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007309/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR055952/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 2T32-DK-007053/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32-AI-007309-22/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR064313/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

