The toll of the gridiron: damage-associated molecular patterns and hypertension in American football
- PMID: 26316270
- PMCID: PMC4684540
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.15-279588
The toll of the gridiron: damage-associated molecular patterns and hypertension in American football
Abstract
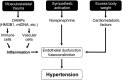
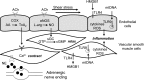
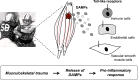
American football has unequivocally been linked to elevations in blood pressure and hypertension, especially in linemen. However, the mechanisms of this increase cannot be attributed solely to increased body weight and associated cardiometabolic risk factors (e.g.,dyslipidemia or hyperglycemia). Therefore, understanding the etiology of football-associated hypertension is essential for improving the quality of life in this mostly young population, as well as for lowering the potential for chronic disease in the future. We propose that inflammatogenic damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) released into the circulation from football-induced musculoskeletal trauma activate pattern-recognition receptors of the innate immune system-specifically, high mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1) and mitochondrial (mt)DNA which activate Toll-like receptor (TLR)4 and -9, respectively. Previously, we observed that circulating levels of these 2 DAMPs are increased in hypertension, and activation of TLR4 and -9 causes endothelial dysfunction and hypertension. Therefore, our novel hypothesis is that musculoskeletal injury from repeated hits in football players, particularly in linemen, leads to elevated circulating HMGB1 and mtDNA to activate TLRs on endothelial cells leading to impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilation, increased vascular tone, and hypertension.
Keywords: blood pressure; inflammation; musculoskeletal trauma.
© FASEB.
Figures
References
-
- Hoffman J. R. (2008) The applied physiology of American football. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 3, 387–392 - PubMed
-
- Pincivero D. M., Bompa T. O. (1997) A physiological review of American football. Sports Med. 23, 247–260 - PubMed
-
- Shankar P. R., Fields S. K., Collins C. L., Dick R. W., Comstock R. D. (2007) Epidemiology of high school and collegiate football injuries in the United States, 2005-2006. Am. J. Sports Med. 35, 1295–1303 - PubMed
-
- Selden M. A., Helzberg J. H., Waeckerle J. F., Browne J. E., Brewer J. H., Monaco M. E., Tang F., O’Keefe J. H. (2009) Cardiometabolic abnormalities in current National Football League players. Am. J. Cardiol. 103, 969–971 - PubMed
-
- Tucker A. M., Vogel R. A., Lincoln A. E., Dunn R. E., Ahrensfield D. C., Allen T. W., Castle L. W., Heyer R. A., Pellman E. J., Strollo P. J. Jr., Wilson P. W., Yates A. P. (2009) Prevalence of cardiovascular disease risk factors among National Football League players. JAMA 301, 2111–2119 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

