Spontaneous Reconstitution of Functional Transmembrane Proteins During Bioorthogonal Phospholipid Membrane Synthesis
- PMID: 26316292
- PMCID: PMC5790194
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201504339
Spontaneous Reconstitution of Functional Transmembrane Proteins During Bioorthogonal Phospholipid Membrane Synthesis
Abstract
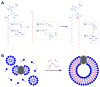
Transmembrane proteins are critical for signaling, transport, and metabolism, yet their reconstitution in synthetic membranes is often challenging. Non-enzymatic and chemoselective methods to generate phospholipid membranes in situ would be powerful tools for the incorporation of membrane proteins. Herein, the spontaneous reconstitution of functional integral membrane proteins during the de novo synthesis of biomimetic phospholipid bilayers is described. The approach takes advantage of bioorthogonal coupling reactions to generate proteoliposomes from micelle-solubilized proteins. This method was successfully used to reconstitute three different transmembrane proteins into synthetic membranes. This is the first example of the use of non-enzymatic chemical synthesis of phospholipids to prepare proteoliposomes.
Keywords: membrane proteins; phospholipids; proteoliposomes; self-assembly; synthetic biology.
© 2015 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
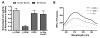


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

