A Possible Role for WNT5A Hypermethylation in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- PMID: 26316480
- PMCID: PMC4451480
- DOI: 10.4274/tjh.2013.0296
A Possible Role for WNT5A Hypermethylation in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
Objective: WNT5A is one of the most studied noncanonical WNT ligands and is shown to be deregulated in different tumor types. Our aim was to clarify whether hypermethylation might be the cause of low WNT5A mRNA levels and whether we could restore this downregulation by reversing the event.
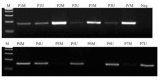
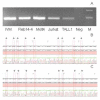
Materials and methods: The expression of WNT5A mRNA was studied in a large acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) patient group (n=86) by quantitative real-time PCR. The methylation status was detected by methylation-specific PCR (MSPCR) and bisulphate sequencing. In order to determine whether methylation has a direct effect on WNT5A expression, disease-representative cell lines were treated by 5'-aza-20-deoxycytidine.
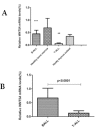
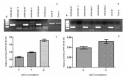
Results: Here we designed a validation experiment of the WNT5A gene, which was previously examined and found to be differentially expressed by microarray study in 31 T-cell ALL patients. The expression levels were confirmed by quantitative real-time PCR and the expression levels were significantly lower in T-cell ALL patients than in control thymic subsets (p=0.007). MSPCR revealed that 86% of the patients were hypermethylated in the WNT5A promoter region. Jurkat and RPMI cell lines were treated with 5'-aza-20-deoxycytidine and WNT5A mRNA expression was restored after treatment.
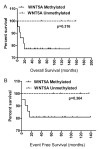
Conclusion: According to our results, WNT5A hypermethylation does occur in ALL patients and it has a direct effect on mRNA expression. Our findings show that epigenetic changes of WNT signaling can play a role in ALL pathogenesis and reversing methylation might be useful as a possible treatment of leukemia.
Amaç: WNT5A, kanonik olmayan WNT ligandlarının en çok çalışılanıdır ve farklı tümör tiplerinde fonksiyon bozukluğu gösterdiği bilinmektedir. Amacımız tespit edilen düşük WNT5A mRNA miktarının altında yatan sebebin hiper metilasyon olup olmadığını açıklığa kavuşturmak ve bu düşüşü hiper metilasyonu tersine çevirerek düzeltip düzeltemeyeceğimizi belirlemekti. Gereç ve Yöntemler: WNT5A mRNA anlatımı, geniş bir ALL hasta gurubunda eş zamanlı kantitatif PZR ile çalışıldı (n=86). Metilasyon durumu metilasyona özgü PZR (MSPZR) ve bisülfit dizileme yöntemleri ile belirlendi. Metilasyonun WNT5A anlatımına doğrudan etkisi olup olmadığı ise hastalık özelliklerini gösteren hücre serilerine 5’-aza-20-deoxycytidine muamelesi ile gösterildi. Bulgular: Bu çalışmada daha önceki çalışmamızda mikro dizi analizi ile belirlenen düşük WNT5A anlatımının doğrulanması için mRNA anlatımı eş zamanlı kantitatif PZR yöntemi ile belirlendi ve T-ALL hastalarında kontrol timositlere göre istatistiki olarak anlamlı bir düşüş gözlendi (p=0,007). MSPZR ise hastaların %86’sında WNT5A geni promotör bölgesinin hiper metile olduğunu gösterdi. Jurkat ve RPMI hücre serileri 5’AZA ile muamele edildi ve WNT5A mRNA anlatımının yeniden arttığı belirlendi. Sonuç: Çalışmamızın sonuçlarına göre ALL hastalarında WNT5A hiper metilasyonu gözlenmektedir ve mRNA anlatımına doğrudan etkisi bulunmaktadır. Sonuçlarımız WNT sinyal ileti yolundaki epigenetik değişikliklerin ALL patogenezinde rol oynadığını göstermektedir ve metilasyonun tersine çevrilmesi lösemiler için olası bir tedavi yöntemi olarak kullanılabilir.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this paper have no conflicts of interest, including specific financial interests, relationships, and/or affiliations relevant to the subject matter or materials included.
Figures

References
-
- Nusse R. WNT targets: repression and activation. Trends Genet. 1999;15:1–3. - PubMed
-
- Dejmek J, Dejmek A, Safholm A, Sjölander A, Andersson T. Wnt-5a protein expression in primary dukes B colon cancers identifies a subgroup of patients with good prognosis. Cancer Res. 2005;65:9142–9146. - PubMed
-
- Huang CL, Liu D, Nakano J, Ishikawa S, Kontani K, Yokomise H, Ueno M. Wnt5a expression is associated with the tumor proliferation and the stromal vascular endothelial growth factor--an expression in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:8765–8773. - PubMed
-
- Saitoh T, Mine T, Katoh M. Frequent up-regulation of WNT5A mRNA in primary gastric cancer. Int J Mol Med. 2002;9:515–519. - PubMed
-
- Saldanha G, Ghura V, Potter L, Fletcher A. Nuclear beta-catenin in basal cell carcinoma correlates with increased proliferation. Br J Dermatol. 2004;151:157–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
