Beneficial and detrimental role of adenosine signaling in diseases and therapy
- PMID: 26316513
- PMCID: PMC4839494
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00350.2015
Beneficial and detrimental role of adenosine signaling in diseases and therapy
Abstract
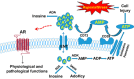
Adenosine is a major signaling nucleoside that orchestrates cellular and tissue adaptation under energy depletion and ischemic/hypoxic conditions by activation of four G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR). The regulation and generation of extracellular adenosine in response to stress are critical in tissue protection. Both mouse and human studies reported that extracellular adenosine signaling plays a beneficial role during acute states. However, prolonged excess extracellular adenosine is detrimental and contributes to the development and progression of various chronic diseases. In recent years, substantial progress has been made to understand the role of adenosine signaling in different conditions and to clarify its significance during the course of disease progression in various organs. These efforts have and will identify potential therapeutic possibilities for protection of tissue injury at acute stage by upregulation of adenosine signaling or attenuation of chronic disease progression by downregulation of adenosine signaling. This review is to summarize current progress and the importance of adenosine signaling in different disease stages and its potential therapeutic effects.
Keywords: adenosine signaling; disease; hypoxia; therapy.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Alencar AK, Pereira SL, Montagnoli TL, Maia RC, Kummerle AE, Landgraf SS, Caruso-Neves C, Ferraz EB, Tesch R, Nascimento JH, de Sant'Anna CM, Fraga CA, Barreiro EJ, Sudo RT, Zapata-Sudo G. Beneficial effects of a novel agonist of the adenosine A2A receptor on monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Br J Pharmacol 169: 953–962, 2013. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ascherio A, Zhang SM, Hernan MA, Kawachi I, Colditz GA, Speizer FE, Willett WC. Prospective study of caffeine consumption and risk of Parkinson's disease in men and women. Ann Neurol 50: 56–63, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Bara-Jimenez W, Sherzai A, Dimitrova T, Favit A, Bibbiani F, Gillespie M, Morris MJ, Mouradian MM, Chase TN. Adenosine A(2A) receptor antagonist treatment of Parkinson's disease. Neurology 61: 293–296, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Bauerle JD, Grenz A, Kim JH, Lee HT, Eltzschig HK. Adenosine generation and signaling during acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 22: 14–20, 2011. - PubMed
-
- Belardinelli L, Shryock JC, Snowdy S, Zhang Y, Monopoli A, Lozza G, Ongini E, Olsson RA, Dennis DM. The A2A adenosine receptor mediates coronary vasodilation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 284: 1066–1073, 1998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

