Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy in liver disease: opportunities and lessons to be learnt?
- PMID: 26316587
- PMCID: PMC4652139
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00036.2015
Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy in liver disease: opportunities and lessons to be learnt?
Abstract
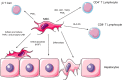
End-stage liver disease is responsible for 30,000 deaths per year in the United States alone, and it is continuing to increase every year. With liver transplantation the only curative treatment currently available, new therapies are in great demand. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) offer an opportunity to both treat liver inflammatory damage, as well as reverse some of the changes that occur following chronic liver injury. With the ability to regulate both the innate and adaptive immune system, as well as both inhibit and promote apoptosis of effector inflammatory cells, there are numerous therapeutic opportunities for MSC in acute and chronic liver disease. This article critically appraises the potential therapeutic roles of MSC in liver disease, as well as the barriers to their adoption into clinical practice.
Keywords: liver disease; mesenchymal stem cell; mesenchymal stromal cell.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood 105: 1815–1822, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Aguilar S, Nye E, Chan J, Loebinger M, Spencer-Dene B, Fisk N, Stamp G, Bonnet D, Janes SM. Murine but not human mesenchymal stem cells generate osteosarcoma-like lesions in the lung. Stem Cells 25: 1586–1594, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Aldridge V, Garg A, Davies N, Bartlett DC, Youster J, Beard H, Kavanagh DP, Kalia N, Frampton J, Lalor PF, Newsome PN. Human mesenchymal stem cells are recruited to injured liver in a β1-integrin and CD44 dependent manner. Hepatology 56: 1063–1073, 2012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

