Refractive cylinder outcomes after calculating toric intraocular lens cylinder power using total corneal refractive power
- PMID: 26316693
- PMCID: PMC4548767
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S88693
Refractive cylinder outcomes after calculating toric intraocular lens cylinder power using total corneal refractive power
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether the total corneal refractive power (TCRP) value, which is based on measurement of both anterior and posterior corneal astigmatism, is effective for toric intraocular lens (IOL) calculation with AcrySof(®) Toric IOLs.
Patients and methods: A consecutive series of cataract surgery cases with AcrySof toric IOL implantation was studied retrospectively. The IOLMaster(®) was used for calculation of IOL sphere, the Pentacam(®) TCRP 3.0 mm apex/ring value was used as the keratometry input to the AcrySof Toric IOL Calculator and the VERION™ Digital Marker for surgical orientation. The keratometry readings from the VERION reference unit were recorded but not used in the actual calculation. Vector differences between expected and actual residual refractive cylinder were calculated and compared to simulated vector errors using the collected VERION keratometry data.
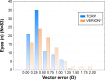
Results: In total, 83 eyes of 56 patients were analyzed. Residual refractive cylinder was 0.25 D or lower in 58% of eyes and 0.5 D or lower in 80% of eyes. The TCRP-based calculation resulted in a statistically significantly lower vector error (P<0.01) and significantly more eyes with a vector error ≤0.5 D relative to the VERION-based calculation (P=0.02). The TCRP and VERION keratometry readings suggested a different IOL toric power in 53/83 eyes. In these 53 eyes the TCRP vector error was lower in 28 cases, the VERION error was lower in five cases, and the error was equal in 20 cases. When the anterior cornea had with-the-rule astigmatism, the VERION was more likely to suggest a higher toric power and when the anterior cornea had against-the-rule astigmatism, the VERION was less likely to suggest a higher toric power.
Conclusion: Using the TCRP keratometry measurement in the AcrySof toric calculator may improve overall postoperative refractive results. Consideration of measured posterior corneal astigmatism, rather than a population-averaged value, appears advantageous.
Keywords: TCRP; astigmatism; biometry; keratometry; posterior corneal astigmatism; toric IOL.
Figures



References
-
- Khan MI, Muhtaseb M. Prevalence of corneal astigmatism in patients having routine cataract surgery at a teaching hospital in the United Kingdom. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011;37(10):1751–1755. - PubMed
-
- Ernest P, Potvin R. Effects of preoperative corneal astigmatism orientation on results with a low-cylinder-power toric intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011;37(4):727–732. - PubMed
-
- Hirnschall N, Gangwani V, Crnej A, Koshy J, Maurino V, Findl O. Correction of moderate corneal astigmatism during cataract surgery: toric intraocular lens versus peripheral corneal relaxing incisions. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2014;40(3):354–361. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed II, Rocha G, Slomovic AR, et al. Canadian Toric Study Group The AcrySof Toric intraocular lens in subjects with cataracts and corneal astigmatism: a randomized, subject-masked, parallel-group, 1-year study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010;36(4):609–616. - PubMed
-
- Holland E, Lane S, Horn JD, Ernest P, Arleo R, Miller KM. The AcrySof Toric intraocular lens in subjects with cataracts and corneal astigmatism: a randomized, subject-masked, parallel-group, 1-year study. Ophthalmology. 2010;117(11):2104–2111. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

