Association between glycemic control and antidiabetic drugs in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with cardiovascular complications
- PMID: 26316711
- PMCID: PMC4547657
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S87294
Association between glycemic control and antidiabetic drugs in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with cardiovascular complications
Abstract
Purpose: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a macrovascular complication in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). To date, glycemic control profiles of antidiabetic drugs in cardiovascular (CV) complications have not been clearly elucidated. Therefore, this study was conducted retrospectively to assess the association of antidiabetic drugs and glycemic control with CV profiles in T2DM patients. The association of concurrent medications and comorbidities with glycemic control was also investigated.
Methods: A total of 220 T2DM patients from the University of Malaya Medical Centre, Malaysia, who had at least one CV complication and who had been taking at least one antidiabetic drug for at least 3 months, were included. The associations of antidiabetics, cardiovascular diseases, laboratory parameters, concurrent medications, comorbidities, demographics, and clinical characteristics with glycemic control were investigated.
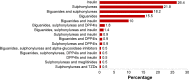
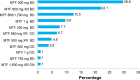
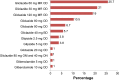
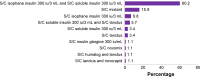
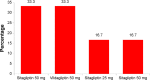
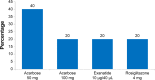
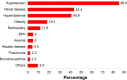
Results: Sulfonylureas in combination (P=0.002) and sulfonylurea monotherapy (P<0.001) were found to be associated with good glycemic control, whereas insulin in combination (P=0.051), and combination biguanides and insulin therapy (P=0.012) were found to be associated with poor glycemic control. Stroke (P=0.044) was the only type of CVD that seemed to be significantly associated with good glycemic control. Other factors such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (P=0.026), elderly patients (P=0.018), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels (P=0.021), and fasting plasma glucose (P<0.001) were found to be significantly correlated with good glycemic control.
Conclusion: Individualized treatment in T2DM patients with CVDs can be supported through a better understanding of the association between glycemic control and CV profiles in T2DM patients.
Keywords: antidiabetic drugs; cardiovascular disease; glycemic control; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycemic control and antidiabetic drugs in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with renal complications.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Aug 7;9:4355-71. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S85676. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26300627 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-existing cardiovascular diseases and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Europe: a matched cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2010 Apr 21;9:15. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-9-15. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2010. PMID: 20409333 Free PMC article.
-
Antidiabetic prescriptions and glycemic control in German patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a retrospective database study.Clin Ther. 2007 Feb;29(2):316-25. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.02.012. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 17472823
-
Is Helicobacter pylori infection associated with glycemic control in diabetics?World J Gastroenterol. 2015 May 7;21(17):5407-16. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i17.5407. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25954115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Divergent effects of various diabetes drugs on cardiovascular prognosis.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2013;14(2-4):e107-22. doi: 10.3909/ricm0671. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2013. PMID: 24448252 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical and Pharmacotherapeutic Profile of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Admitted to a Hospital Emergency Department.Biomedicines. 2023 Jan 18;11(2):256. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020256. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36830792 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and factors associated with periodontal disease in patients with diabetes mellitus attending Kiruddu National Referral Hospital, Uganda.Pan Afr Med J. 2022 Dec 23;43:202. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2022.43.202.35971. eCollection 2022. Pan Afr Med J. 2022. PMID: 36942143 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Renal Microcirculation in Progression of Chronic Kidney Injury in Obesity.Am J Nephrol. 2016;44(5):354-367. doi: 10.1159/000452365. Epub 2016 Oct 22. Am J Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27771702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determinants of poor glycemic control among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients at University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia: Unmatched case-control study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 9;14:1087437. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1087437. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36843610 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetic retinopathy in the Eastern Morocco: Different stage frequencies and associated risk factors.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021 Jan;28(1):775-784. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.11.010. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33424367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . Diabetes Atlas. 5th ed. Brussels, Belgium: IDF; 2011.
-
- Wan Nazaimoon WM, Md Isa SH, Wan Mohamad WB, et al. Prevalence of diabetes in Malaysia and usefulness of HbA1C as a diagnostic criterion. Diabet Med. 2013;30(7):825–828. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2014;36:S14–S87. - PubMed
-
- World Heart Federation . Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: Diabetes. Geneva, Switzerland: World Heart Federation; 2014. [Accessed March 26, 2014]. Available from: http://www.world-heart-federation.org/cardiovascular-health/cardiovascul...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

