Does multicomponent physical exercise with simultaneous cognitive training boost cognitive performance in older adults? A 6-month randomized controlled trial with a 1-year follow-up
- PMID: 26316729
- PMCID: PMC4544626
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S87732
Does multicomponent physical exercise with simultaneous cognitive training boost cognitive performance in older adults? A 6-month randomized controlled trial with a 1-year follow-up
Abstract
Background: Cognitive impairment is a health problem that concerns almost every second elderly person. Physical and cognitive training have differential positive effects on cognition, but have been rarely applied in combination. This study evaluates synergistic effects of multicomponent physical exercise complemented with novel simultaneous cognitive training on cognition in older adults. We hypothesized that simultaneous cognitive-physical components would add training specific cognitive benefits compared to exclusively physical training.
Methods: Seniors, older than 70 years, without cognitive impairment, were randomly assigned to either: 1) virtual reality video game dancing (DANCE), 2) treadmill walking with simultaneous verbal memory training (MEMORY), or 3) treadmill walking (PHYS). Each program was complemented with strength and balance exercises. Two 1-hour training sessions per week over 6 months were applied. Cognitive performance was assessed at baseline, after 3 and 6 months, and at 1-year follow-up. Multiple regression analyses with planned comparisons were calculated.
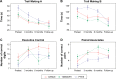
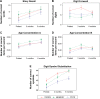
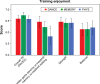
Results: Eighty-nine participants were randomized to the three groups initially, 71 completed the training, while 47 were available at 1-year follow-up. Advantages of the simultaneous cognitive-physical programs were found in two dimensions of executive function. "Shifting attention" showed a time×intervention interaction in favor of DANCE/MEMORY versus PHYS (F[2, 68] =1.95, trend P=0.075, r=0.17); and "working memory" showed a time×intervention interaction in favor of DANCE versus MEMORY (F[1, 136] =2.71, trend P=0.051, R (2)=0.006). Performance improvements in executive functions, long-term visual memory (episodic memory), and processing speed were maintained at follow-up in all groups.
Conclusion: Particular executive functions benefit from simultaneous cognitive-physical training compared to exclusively physical multicomponent training. Cognitive-physical training programs may counteract widespread cognitive impairments in the elderly.
Keywords: cognitive impairment; dance; elderly; executive function; transfer; video game.
Figures

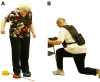
References
-
- Scafato E, Gandin C, Galluzzo L, et al. PR.E.A. Working Group (Italian PRoject on Epidemiology of Alzheimer’s disease) Prevalence of aging-associated cognitive decline in an Italian elderly population: results from cross-sectional phase of Italian PRoject on Epidemiology of Alzheimer’s disease (IPREA) Aging Clin Exp Res. 2010;22(5–6):440–449. - PubMed
-
- Lautenschlager NT, Cox K, Cyarto EV. The influence of exercise on brain aging and dementia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1822(3):474–481. - PubMed
-
- Gregory MA, Gill DP, Petrella RJ. Brain health and exercise in older adults. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2013;12(4):256–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

