Efficacy and safety of the long-acting β2-agonist olodaterol over 4 weeks in Japanese patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- PMID: 26316741
- PMCID: PMC4548739
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S86002
Efficacy and safety of the long-acting β2-agonist olodaterol over 4 weeks in Japanese patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Abstract
Background: Olodaterol is a novel long-acting β2-agonist with proven ≥24-hour duration of action in preclinical and clinical studies.
Objective: This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study evaluated the dose response of once-daily (QD) olodaterol based on bronchodilator efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics over 4 weeks in Japanese patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
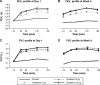
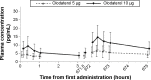
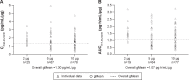
Methods: All eligible patients were randomized to receive 2 µg, 5 µg, or 10 µg of olodaterol or placebo for 4 weeks via the Respimat Soft Mist inhaler. The primary end point was the change from baseline in trough forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) after 4 weeks of olodaterol treatment. Secondary end points included trough FEV1 after 1 week and 2 weeks of treatment, FEV1 area under the curve from 0 hour to 3 hours (AUC(0-3)), peak FEV1 from 0 hour to 3 hours (peak FEV1), and corresponding forced vital capacity (FVC) responses. Rescue medication use, COPD symptoms, physician global evaluation, pharmacokinetics, and safety were also assessed.
Results: A total of 328 patients with COPD were randomized to receive treatment. All olodaterol doses assessed in the study showed statistically significant increases in trough FEV1 compared to placebo at Day 29 (P<0.0001). Mean increases in peak FEV1 and FEV1 AUC(0-3) compared to placebo were also significant (P<0.0001). A clear dose-response relationship was observed across all treatment groups. FVC responses (trough and FVC AUC(0-3)) supported FEV1 outcomes. All doses of olodaterol were well tolerated, and no safety concerns were identified.
Conclusion: QD olodaterol demonstrated 24-hour bronchodilator efficacy and was well tolerated in Japanese patients with COPD.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT00824382.
Keywords: dose-finding; once-daily; plasma concentration; pulmonary function; trough FEV1; trough FVC.
Figures

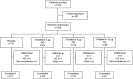

References
-
- Pauwels RA, Buist AS, Calverley PMA, Jenkins CR, Hurd SS, GOLD Scientific ommittee Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. NHLBI/WHO Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Workshop Summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163(5):1256–1276. - PubMed
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. [Accessed February 17, 2015]. Updated 2013. Available from: http://www.goldcopd.org/uploads/users/files/GOLD_Report_2013_Feb20.pdf.
-
- Boyd G, Morice AH, Pounsford JC, Siebert M, Peslis N, Crawford C. An evaluation of salmeterol in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Eur Respir J. 1997;10(4):815–821. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

