Nanotechnology for treating osteoporotic vertebral fractures
- PMID: 26316746
- PMCID: PMC4540116
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S85037
Nanotechnology for treating osteoporotic vertebral fractures
Abstract
Osteoporosis is a serious public health problem affecting hundreds of millions of aged people worldwide, with severe consequences including vertebral fractures that are associated with significant morbidity and mortality. To augment or treat osteoporotic vertebral fractures, a number of surgical approaches including minimally invasive vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty have been developed. However, these approaches face problems and difficulties with efficacy and long-term stability. Recent advances and progress in nanotechnology are opening up new opportunities to improve the surgical procedures for treating osteoporotic vertebral fractures. This article reviews the improvements enabled by new nanomaterials and focuses on new injectable biomaterials like bone cements and surgical instruments for treating vertebral fractures. This article also provides an introduction to osteoporotic vertebral fractures and current clinical treatments, along with the rationale and efficacy of utilizing nanomaterials to modify and improve biomaterials or instruments. In addition, perspectives on future trends with injectable bone cements and surgical instruments enhanced by nanotechnology are provided.
Keywords: bone cement; kyphoplasty; nanomaterials; osteoporosis; pedicle screw; radiopacifier; vertebral fracture.
Figures

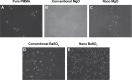
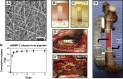
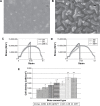
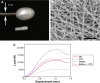

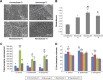
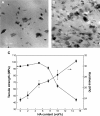
References
-
- Cummings SR, Black DM, Rubin SM. Lifetime risks of hip, Colles, or vertebral fracture and coronary heart disease among white postmenopausal women. Arch Intern Med. 1989;149:2445–2448. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Assessment of fracture risk and its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Report of a WHO Study Group. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 1994;843:1–129. - PubMed
-
- Messina C, Bandirali M, Sconfienza LM. Prevalence and type of errors in dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. Eur Radiol. 2015;25:1504–1511. - PubMed
-
- Conversano F, Franchini R, Greco A. A Novel ultrasound methodology for estimating spine mineral density. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41:281–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

