CAG repeat polymorphisms in the androgen receptor and breast cancer risk in women: a meta-analysis of 17 studies
- PMID: 26316780
- PMCID: PMC4540135
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S85130
CAG repeat polymorphisms in the androgen receptor and breast cancer risk in women: a meta-analysis of 17 studies
Abstract
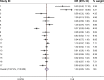
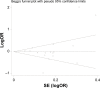
The association between polymorphic CAG repeats in the androgen receptor gene in women and breast cancer susceptibility has been studied extensively. However, the conclusions regarding this relationship remain conflicting. The purpose of this meta-analysis was to identify whether androgen receptor CAG repeat lengths were related to breast cancer susceptibility. The MEDLINE, PubMed, and EMBASE databases were searched through to December 2014 to identify eligible studies. Data and study quality were rigorously assessed by two investigators according to the Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale. The publication bias was assessed by the Begg's test. Seventeen eligible studies were included in this meta-analysis. The overall analysis suggested no association between CAG polymorphisms and breast cancer risk (odds ratio [OR] 1.031, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.855-1.245). However, in the subgroup analysis, we observed that long CAG repeats significantly increased the risk of breast cancer in the Caucasian population (OR 1.447, 95% CI 1.089-1.992). Additionally, the risk was significantly increased in Caucasian women carrying two alleles with CAG repeats ≥22 units compared with those with two shorter alleles (OR 1.315, 95% CI 1.014-1.707). These findings suggest that long CAG repeats increase the risk of breast cancer in Caucasian women. However, larger scale case-control studies are needed to validate our results.
Keywords: CAG repeat polymorphism; androgen; breast cancer; meta-analysis; risk; women.
Figures



References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Giguere Y, Dewailly E, Brisson J, et al. Short polyglutamine tracts in the androgen receptor are protective against breast cancer in the general population. Cancer Res. 2001;61:5869–5874. - PubMed
-
- Given HF, Radbourne R, Oag H, et al. The androgen receptor exon 1 trinucleotide repeat does not act as a modifier of the age of presentation in breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2000;36:533–534. - PubMed
-
- Dagan E, Friedman E, Paperna T, Carmi N, Gershoni-Baruch R. Androgen receptor CAG repeat length in Jewish Israeli women who are BRCA1/2 mutation carriers: association with breast/ovarian cancer phenotype. Eur J Hum Genet. 2002;10:724–728. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

