Merkel cell carcinoma of the head and neck: pathogenesis, current and emerging treatment options
- PMID: 26316785
- PMCID: PMC4548751
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S72202
Merkel cell carcinoma of the head and neck: pathogenesis, current and emerging treatment options
Abstract
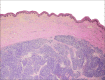
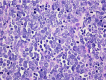
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a relatively uncommon, neuroendocrine, cutaneous malignancy that often exhibits clinically aggressive features and is associated with a poor prognosis. It typically presents as a painless, rapidly enlarging, dome-shaped red or purplish nodule in a sun-exposed area of the head and neck or upper extremities. Our understanding of MCC has increased dramatically over the last several years and the pathogenesis continues to be an area of active research. The etiology is likely multifactorial with immunosuppression, UV-induced skin damage, and viral factors contributing to the development of MCC. The recent discovery of Merkel cell polyomavirus has allowed for at least one aspect of disease development to be much better understood. In most cases, treatment consists of wide local excision with adjuvant radiation therapy. The role of chemotherapeutics is still being defined. The recent advancement of knowledge regarding the pathogenesis of MCC has led to an explosion research into novel therapeutic agents and strategies. This review seeks to summarize the current body of literature regarding the pathogenesis of MCC and potential targets for future therapies.
Keywords: Merkel cells; neuroendocrine cancer; polyomavirus; skin cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Merkel F. Tastzellen and Tastkörperchen bei den Hausthieren und beim Menschen. Arch Mikrosk Anat. 1875;11:636.
-
- Toker C. Trabecular carcinoma of the skin. Arch Dermatol. 1972;105(1):107–110. - PubMed
-
- Tang CK, Toker C. Trabecular carcinoma of the skin: an ultrastructural study. Cancer. 1978;42(5):2311–2321. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

