Chronic pain in hypermobility syndrome and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (hypermobility type): it is a challenge
- PMID: 26316810
- PMCID: PMC4548768
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S64251
Chronic pain in hypermobility syndrome and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (hypermobility type): it is a challenge
Abstract
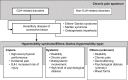
Generalized joint hypermobility (GJH) is highly prevalent among patients diagnosed with chronic pain. When GJH is accompanied by pain in ≥4 joints over a period ≥3 months in the absence of other conditions that cause chronic pain, the hypermobility syndrome (HMS) may be diagnosed. In addition, GJH is also a clinical sign that is frequently present in hereditary diseases of the connective tissue, such as the Marfan syndrome, osteogenesis imperfecta, and the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. However, within the Ehlers-Danlos spectrum, a similar subcategory of patients having similar clinical features as HMS but lacking a specific genetic profile was identified: Ehlers-Danlos syndrome hypermobility type (EDS-HT). Researchers and clinicians have struggled for decades with the highly diverse clinical presentation within the HMS and EDS-HT phenotypes (Challenge 1) and the lack of understanding of the pathological mechanisms that underlie the development of pain and its persistence (Challenge 2). In addition, within the HMS/EDS-HT phenotype, there is a high prevalence of psychosocial factors, which again presents a difficult issue that needs to be addressed (Challenge 3). Despite recent scientific advances, many obstacles for clinical care and research still remain. To gain further insight into the phenotype of HMS/EDS-HT and its mechanisms, clearer descriptions of these populations should be made available. Future research and clinical care should revise and create consensus on the diagnostic criteria for HMS/EDS-HT (Solution 1), account for clinical heterogeneity by the classification of subtypes within the HMS/EDS-HT spectrum (Solution 2), and create a clinical core set (Solution 3).
Keywords: Ehlers-Danlos hypermobility type; chronic musculoskeletal pain; generalized joint hypermobility; hypermobility syndrome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Generalized Hyperalgesia in Children and Adults Diagnosed With Hypermobility Syndrome and Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Hypermobility Type: A Discriminative Analysis.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2017 Mar;69(3):421-429. doi: 10.1002/acr.22998. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2017. PMID: 27483212
-
Differential diagnosis and diagnostic flow chart of joint hypermobility syndrome/ehlers-danlos syndrome hypermobility type compared to other heritable connective tissue disorders.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2015 Mar;169C(1):6-22. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31429. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2015. PMID: 25821090 Review.
-
Lack of consensus on tests and criteria for generalized joint hypermobility, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: hypermobile type and joint hypermobility syndrome.Am J Med Genet A. 2014 Mar;164A(3):591-6. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36402. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Am J Med Genet A. 2014. PMID: 24464988
-
Knowledge, assessment, and management of adults with joint hypermobility syndrome/Ehlers-Danlos syndrome hypermobility type among Flemish physiotherapists.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2015 Mar;169C(1):76-83. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31434. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2015. PMID: 25821093
-
Cognitive, emotional, and behavioral considerations for chronic pain management in the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome hypermobility-type: a narrative review.Disabil Rehabil. 2019 May;41(9):1110-1118. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2017.1419294. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Disabil Rehabil. 2019. PMID: 29357706 Review.
Cited by
-
Systemic manifestations of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2020 Aug 26;34(1):49-53. doi: 10.1080/08998280.2020.1805714. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2020. PMID: 33456144 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological interventions for individuals with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and hypermobility spectrum disorder: a scoping review.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2023 Aug 31;18(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s13023-023-02799-y. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2023. PMID: 37653505 Free PMC article.
-
Does joint hypermobility exacerbate altered landing and jumping strategies in adolescents with fibromyalgia syndrome compared to controls?Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2025 Apr;124:106466. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2025.106466. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2025. PMID: 40048834
-
Respiratory Manifestations and Their Physical, Psychological, and Social Impacts in Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes and Generalized Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 11;14(12):4126. doi: 10.3390/jcm14124126. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40565873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Navigating the psychosocial landscape of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: an autobiographic case study.Discov Ment Health. 2025 Aug 17;5(1):123. doi: 10.1007/s44192-025-00268-5. Discov Ment Health. 2025. PMID: 40820186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grahame R. Hypermobility: an important but often neglected area within rheumatology. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2008;4(10):522–524. - PubMed
-
- Grahame R, Bird HA, Child A. The revised (Brighton 1998) criteria for the diagnosis of benign joint hypermobility syndrome (BJHS) J Rheumatol. 2000;27(7):1777–1779. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical