Progress toward overcoming hypoxia-induced resistance to solid tumor therapy
- PMID: 26316817
- PMCID: PMC4542411
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S58285
Progress toward overcoming hypoxia-induced resistance to solid tumor therapy
Abstract
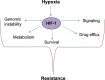
Hypoxic tumors are associated with poor clinical outcome for multiple types of human cancer. This may be due, in part, to hypoxic cancer cells being resistant to anticancer therapy, including radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy. Hypoxia inducible factor 1, a major regulator of cellular response to hypoxia, regulates the expression of genes that are involved in multiple aspects of cancer biology, including cell survival, proliferation, metabolism, invasion, and angiogenesis. Here, we review multiple pathways regulated by hypoxia/hypoxia inducible factor 1 in cancer cells and discuss the latest advancements in overcoming hypoxia-mediated tumor resistance.
Keywords: HIF-1; apoptosis; cancer; chemoresistance; signaling.
Figures
References
-
- Brahimi-Horn MC, Chiche J, Pouysségur J. Hypoxia and cancer. J Mol Med (Berl) 2007;85(12):1301–1307. - PubMed
-
- Vaupel P, Mayer A. Hypoxia in cancer: significance and impact on clinical outcome. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007;26(2):225–239. - PubMed
-
- Moeller BJ, Richardson RA, Dewhirst MW. Hypoxia and radiotherapy: opportunities for improved outcomes in cancer treatment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007;26(2):241–248. - PubMed
-
- Shannon AM, Bouchier-Hayes DJ, Condron CM, Toomey D. Tumour hypoxia, chemotherapeutic resistance and hypoxia-related therapies. Cancer Treat Rev. 2003;29(4):297–307. - PubMed
-
- Ellis LM, Hicklin DJ. Resistance to Targeted Therapies: Refining Anticancer Therapy in the Era of Molecular Oncology. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(24):7471–7478. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

