Negative pressure pulmonary edema after nasal fracture reduction in an obese female patient: a case report
- PMID: 26316826
- PMCID: PMC4547658
- DOI: 10.2147/IMCRJ.S86099
Negative pressure pulmonary edema after nasal fracture reduction in an obese female patient: a case report
Abstract
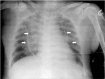
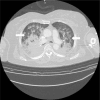
Postoperative negative pressure pulmonary edema (NPPE) is a rare, but well-known life-threatening complication of acute upper airway obstruction (UAO) which develops after general anesthesia. The pronounced inspiratory efforts following UAO lead to excessive negative inspiratory pressure, which may cause acute pulmonary edema. Early recognition and prompt treatment of NPPE is necessary to prevent patient morbidity and mortality. In addition, the physician should carefully manage the patient who has risk factors of UAO to prevent this situation. We experienced a case of NPPE following laryngospasm after tracheal extubation in an obese patient who underwent open reduction of orbital wall and nasal bone surgery.
Keywords: airway obstruction; laryngospasm; nasal surgery; negative pressure pulmonary edema; obese.
Figures

References
-
- Patton WC, Baker CL., Jr Prevalence of negative-pressure pulmonary edema at an orthopaedic hospital. J South Orthop Assoc. 2000;9(4):248–253. - PubMed
-
- Tami TA, Chu F, Wildes TO, Kaplan M. Pulmonary edema and acute upper airway obstruction. Laryngoscope. 1986;96(5):506–509. - PubMed
-
- Louis PJ, Fernandes R. Negative pressure pulmonary edema. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;93(1):4–6. - PubMed
-
- Krodel DJ, Bittner EA, Abdulnour R, Brown R, Eikermann M. Case scenario: acute postoperative negative pressure pulmonary edema. Anesthesiology. 2010;113(1):200–207. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

