Against Lung Cancer Cells: To Be, or Not to Be, That Is the Problem
- PMID: 26316936
- PMCID: PMC4437407
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/659365
Against Lung Cancer Cells: To Be, or Not to Be, That Is the Problem
Abstract
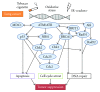
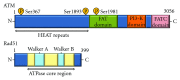
Tobacco smoke and radioactive radon gas impose a high risk for lung cancer. The radon-derived ionizing radiation and some components of cigarette smoke induce oxidative stress by generating reactive oxygen species (ROS). Respiratory lung cells are subject to the ROS that causes DNA breaks, which subsequently bring about DNA mutagenesis and are intimately linked with carcinogenesis. The damaged cells by oxidative stress are often destroyed through the active apoptotic pathway. However, the ROS also perform critical signaling functions in stress responses, cell survival, and cell proliferation. Some molecules enhance radiation-induced tumor cell killing via the reduction in DNA repair levels. Hence the DNA repair levels may be a novel therapeutic modality in overcoming drug resistance in lung cancer. Either survival or apoptosis, which is determined by the balance between DNA damage and DNA repair levels, may lender the major problems in cancer therapy. The purpose of this paper is to take a closer look at risk factor and at therapy modulation factor in lung cancer relevant to the ROS.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cancer risk and oxidative DNA damage in man.J Mol Med (Berl). 1996 Jun;74(6):297-312. doi: 10.1007/BF00207507. J Mol Med (Berl). 1996. PMID: 8862511 Review.
-
Oxidative DNA damage is involved in cigarette smoke-induced lung injury in rats.Environ Health Prev Med. 2015 Sep;20(5):318-24. doi: 10.1007/s12199-015-0469-z. Epub 2015 May 13. Environ Health Prev Med. 2015. PMID: 25967734 Free PMC article.
-
Three components of cigarette smoke altered the growth and apoptosis of metastatic colon cancer cells via inducing the synthesis of reactive oxygen species and endoplasmic reticulum stress.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016 Jul;45:80-9. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2016.05.016. Epub 2016 May 20. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27262990
-
MTH1 deficiency selectively increases non-cytotoxic oxidative DNA damage in lung cancer cells: more bad news than good?BMC Cancer. 2018 Apr 16;18(1):423. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4332-7. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29661172 Free PMC article.
-
The role of oxidative stress in the biological responses of lung epithelial cells to cigarette smoke.Biomarkers. 2009 Jul;14 Suppl 1:90-6. doi: 10.1080/13547500902965047. Biomarkers. 2009. PMID: 19604067 Review.
Cited by
-
Connection between Tumor Suppressor BRCA1 and PTEN in Damaged DNA Repair.Front Oncol. 2014 Nov 10;4:318. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00318. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25426449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Combination Of Weak Expression Of PRDX4 And Very High MIB-1 Labelling Index Independently Predicts Shorter Disease-free Survival In Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma.Int J Med Sci. 2018 Jun 14;15(10):1025-1034. doi: 10.7150/ijms.25734. eCollection 2018. Int J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30013444 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of PRDX4 and the EGFR mutation status on cellular proliferation in lung adenocarcinoma.Int J Med Sci. 2019 Aug 14;16(9):1199-1206. doi: 10.7150/ijms.36071. eCollection 2019. Int J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31588184 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-203a-3p regulates the biological behaviors of ovarian cancer cells through mediating the Akt/GSK-3β/Snail signaling pathway by targeting ATM.J Ovarian Res. 2019 Jul 5;12(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13048-019-0532-2. J Ovarian Res. 2019. PMID: 31277702 Free PMC article.
-
NFATc2 enhances tumor-initiating phenotypes through the NFATc2/SOX2/ALDH axis in lung adenocarcinoma.Elife. 2017 Jul 24;6:e26733. doi: 10.7554/eLife.26733. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28737489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Britton J. Passive smoking damages children's health. Practitioner. 2010;254(1729):27–30. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

