Analysis of Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A and Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1alpha in Patients Operated on Stage I Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 26316946
- PMCID: PMC4437402
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/810786
Analysis of Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A and Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1alpha in Patients Operated on Stage I Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
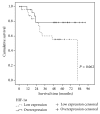
Objectives. Recent studies show that expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1α) favours expression of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A), and these biomarkers are linked to cellular proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis in different cancers. We analyze expression of HIF-1α and VEGF-A to clinicopathologic features and survival of patients operated on stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Methodology. Prospective study of 52 patients operated on with stage I. Expression of VEGF-A and HIF-1α was performed through real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Results. Mean age was 64.7 and 86.5% of patients were male. Stage IA represented 23.1% and stage IB 76.9%. Histology classification was 42.3% adenocarcinoma, 34.6% squamous cell carcinoma, and 23.1% others. Median survival was 81.0 months and 5-year survival 67.2%. There was correlation between HIF-1α and VEGF-A (P = 0.016). Patients with overexpression of HIF-1α had a tendency to better survival with marginal statistical significance (P = 0.062). Patients with overexpression of VEGF-A had worse survival, but not statistically significant (P = 0.133). Conclusion. The present study revealed that VEGF-A showed correlation with HIF-1α. HIF-1α had a tendency to protective effect with a P value close to statistical significance. VEGF-A showed a contrary effect but without statistical significance.
Figures


References
-
- Fernández E. ., Borrás J. M., Levi F., Schiaffino A., García M., Vecchia C. Mortalidad por cáncer en España. Medicina Clinica. 2000;114:449–451. - PubMed
-
- Encuentra A. L., Ríos F. L., Conde E., et al. Composite anatomical-clinical-molecular prognostic model in non-small cell lung cancer. The European Respiratory Journal. 2011;37:136–142. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

