Monitoring HIV Epidemic in Pregnant Women: Are the Current Measures Enough?
- PMID: 26316980
- PMCID: PMC4437413
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/194831
Monitoring HIV Epidemic in Pregnant Women: Are the Current Measures Enough?
Abstract
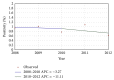
Introduction. Burden of HIV in pregnant women follows overall epidemic in India. Hence, it is imperative that prevalence calculations in this group be accurate. The present study was carried out to determine prevalence of HIV in pregnant women attending our hospital, to determine trend of HIV infection and to compare our results with reported prevalence. Methods. All pregnant women are routinely counselled for HIV testing using opt-out strategy. Year-wise positivity and trend were determined in these patients over a period of five years. The positivity in different age groups was determined. Results. 31,609 women were tested of which 279 (0.88%) were positive. Positivity showed a declining trend over study period and significant quadratic trend (biphasic, P < 0.05) was observed. The positivity in older age group ≥35 years (1.64%) was significantly more than younger age groups (0.76% in 15-24-year and 0.94% in 25-34-year age group) (P = 0.0052). Conclusion. A significant decline in HIV positivity was seen over the study period. Taking into account heterogeneous nature of HIV epidemic even within the same district, analysis at local levels especially using the prevention of parent to child transmission of HIV program data is critical for HIV programming and resource allocation.
Figures
References
-
- Simoes E. A., Babu P. G., John T. J., et al. Evidence for HTLV-III infection in prostitutes in Tamil Nadu (India). The Indian journal of medical research. 1987;85:335–338. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization and Joint United Nations Programmes on HIV/AIDS. AIDS Epidemic Update. 2006. http://www.who.int/hiv/mediacentre/2006_EpiUpdate_en.pdf.
-
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Second Generation HIV Surveillance: An Update: Know Your Epidemic. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2013. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/85511/1/9789241505826_eng.pdf. - PubMed
-
- Ashtagi G. S., Metgud C. S., Walvekar P. R., Naik V. A. Prevalence of HIV among rural pregnant women attending PPTCT services at KLE Hospital, Belgaum. Al Ameen Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011;4(1):45–48.
-
- National Strategic Plan. Muli-Drug ARV for Prevention of Parent to Child Transmission of HIV (PPTCT) under National AIDS Control Programme in India. 2013. http://www.naco.gov.in/upload/NACP%20-%20IV/18022014%20BSD/National%20St....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources