Towards the Elimination of Syphilis in a Small Developing Country
- PMID: 26316981
- PMCID: PMC4519538
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/801437
Towards the Elimination of Syphilis in a Small Developing Country
Abstract
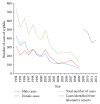
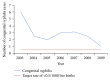
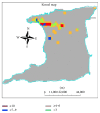
Objective. To describe the current epidemiological features of syphilis and congenital syphilis in Trinidad, 2009-2012. Methods. All laboratory confirmed syphilis cases diagnosed through a vertical program in the Ministry of Health, between 1/1/2009 and 31/12/2012, were identified. All relevant data were collected including address which was geocoded and mapped using ArcGIS 10.0 (Esri). Both spatial techniques and standardized incidence ratios were used to determine hot spots. Results. The annual cumulative incidence rate for syphilis remains high varying from 39 per 100 000 population in 2009 to 29 per 100 000 in 2012. We identified 3 "hot spots," in urban areas of Trinidad. Young men and particularly young women in childbearing age 15-35 living in urban high density populations were commonly infected groups. Conclusion. The incidence of syphilis continues to be very high in Trinidad. New initiatives will have to be formulated in order to attain the global initiative to eradicate syphilis by 2015.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. The Global Elimination of Congenital Syphilis: Rationale and Strategy for Action. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2007. http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/rtis/9789241595858/en....
-
- UNAIDS. Global Plan towards the Elimination of New HIV Infections among Children by 2015 and Keeping Their Mothers Alive 2011–2015 (4) 2015. - PubMed
-
- Pan American Health Organization. Regional Initiative for the Elimination of Vertical Transmission of HIV and Congenital Syphilis in Latin America and the Caribbean: Regional Monitoring Strategy. Pan American Health Organization; 2010. http://new.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_docman&task=doc_view&gid=694...
-
- CARICOM Health Ministers Launch Regional Initiative for HIV and Syphilis Free Generations 2015 Deadline to End Mother-to-Child Transmission of HIV and Congenital Syphilis, http://new.paho.org/hq/dmdocuments/2009/Caribbean%20press%20release%20ab....
-
- CDC. Syphilis (Treponema pallidium): 2014 Case Definitions. CDC, National Notifiable Disease Surveillance System (NNDSS); 2014. http://wwwn.cdc.gov/nndss/script/casedef.aspx?condyrid=941&datepub=1/1/2014.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

