Censored Data Analysis Reveals Effects of Age and Hepatitis C Infection on C-Reactive Protein Levels in Healthy Adult Chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes)
- PMID: 26317021
- PMCID: PMC4437358
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/709740
Censored Data Analysis Reveals Effects of Age and Hepatitis C Infection on C-Reactive Protein Levels in Healthy Adult Chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes)
Abstract
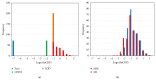
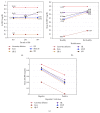
C-reactive protein, a conserved acute-phase protein synthesized in the liver and involved in inflammation, infection, and tissue damage, is an informative biomarker for human cardiovascular disease. Out of 258 captive adult common chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) assayed for CRP, 27.9% of the data were below the quantitation limit. Data were analyzed by the Kaplan-Meier method and results compared to other methods for handling censored data (including deletion, replacement, and imputation). Kaplan-Meier results demonstrated a modest age effect and a strong effect of HCV infection in reducing CRP but did not allow inference of reference intervals. Results of other methods varied considerably. Substitution schemes differed widely in statistical significance, with estimated group means biased by the size of the substitution constant, while inference of unbiased reference intervals was impossible. Single imputation gave reasonable statistical inferences but unreliable reference intervals. Multiple imputation gave reliable results, for both statistical inference and reference intervals, and was comparable to the Kaplan-Meier standard. Other methods should be avoided. CRP did not predict cardiovascular disease, but CRP levels were reduced by 50% in animals with hepatitis C infection and showed inverse relationships with 2 liver function enzymes. Results suggested that hsCRP can be an informative biomarker of chronic hepatic dysfunction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Normal C-reactive protein values for captive chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes).Contemp Top Lab Anim Sci. 2005 Sep;44(5):25-6. Contemp Top Lab Anim Sci. 2005. PMID: 16138777
-
Determination of hemoglobin A1c and fasting blood glucose reference intervals in captive chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes).J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2011 Mar;50(2):165-70. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2011. PMID: 21439208 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
A multiple imputation method based on weighted quantile regression models for longitudinal censored biomarker data with missing values at early visits.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018 Jan 11;18(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12874-017-0463-9. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018. PMID: 29325529 Free PMC article.
-
A critical role for the chimpanzee model in the study of hepatitis C.Hepatology. 2004 Jun;39(6):1469-75. doi: 10.1002/hep.20268. Hepatology. 2004. PMID: 15185284 Review.
Cited by
-
Missing data in bioarchaeology II: A test of ordinal and continuous data imputation.Am J Biol Anthropol. 2022 Nov;179(3):349-364. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.24614. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Am J Biol Anthropol. 2022. PMID: 36790608 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related physiological dysregulation progresses slowly in semi-free-ranging chimpanzees.Evol Med Public Health. 2024 Jun 19;12(1):129-142. doi: 10.1093/emph/eoae010. eCollection 2024. Evol Med Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39239461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Du Clos T. W. Function of C-reactive protein. Annals of Medicine. 2000;32(4):274–278. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

