The Effects of Sex and Chronic Restraint on Instrumental Learning in Rats
- PMID: 26317104
- PMCID: PMC4437261
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/893126
The Effects of Sex and Chronic Restraint on Instrumental Learning in Rats
Abstract
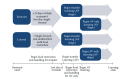
Chronic stress has been shown to impact learning, but studies have been sparse or nonexistent examining sex or task differences. We examined the effects of sex and chronic stress on instrumental learning in adult rats. Rats were tested in an aversive paradigm with or without prior appetitive experience, and daily body weight data was collected as an index of stress. Relative to control animals, reduced body weight was maintained across the stress period for males (-7%, P ≤ .05) and females (-5%, P ≤ .05). For males, there were within-subject day-by-day differences after asymptotic transition, and all restrained males were delayed in reaching asymptotic performance. In contrast, stressed females were facilitated in appetitive and aversive-only instrumental learning but impaired during acquisition of the aversive transfer task. Males were faster than females in reaching the appetitive shaping criterion, but females were more efficient in reaching the appetitive tone-signaled criterion. Finally, an effect of task showed that while females reached aversive shaping criterion at a faster rate when they had prior appetitive learning, they were impaired in tone-signaled avoidance learning only when they had prior appetitive learning. These tasks reveal important nuances on the effect of stress and sex differences on goal-directed behavior.
Figures





References
-
- McEwen B. S., Seeman T. Protective and damaging effects of mediators of stress. Elaborating and testing the concepts of allostasis and allostatic load. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1999;896:30–47. - PubMed
-
- Sandi C., Davies H. A., Cordero M. I., Rodriguez J. J., Popov V. I., Stewart M. G. Rapid reversal of stress induced loss of synapses in CA3 of rat hippocampus following water maze training. European Journal of Neuroscience. 2003;17(11):2447–2456. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02675.x. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

