A synthetic peptide targeting the BH4 domain of Bcl-2 induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma and follicular lymphoma cells alone or in combination with agents targeting the BH3-binding pocket of Bcl-2
- PMID: 26317541
- PMCID: PMC4694997
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4489
A synthetic peptide targeting the BH4 domain of Bcl-2 induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma and follicular lymphoma cells alone or in combination with agents targeting the BH3-binding pocket of Bcl-2
Abstract
Bcl-2 inhibits apoptosis by two distinct mechanisms but only one is targeted to treat Bcl-2-positive malignancies. In this mechanism, the BH1-3 domains of Bcl-2 form a hydrophobic pocket, binding and inhibiting pro-apoptotic proteins, including Bim. In the other mechanism, the BH4 domain mediates interaction of Bcl-2 with inositol 1,4, 5-trisphosphate receptors (IP3Rs), inhibiting pro-apoptotic Ca2+ signals. The current anti-Bcl-2 agents, ABT-263 (Navitoclax) and ABT-199 (Venetoclax), induce apoptosis by displacing pro-apoptotic proteins from the hydrophobic pocket, but do not inhibit Bcl-2-IP3R interaction. Therefore, to target this interaction we developed BIRD-2 (Bcl-2 IP3 Receptor Disruptor-2), a decoy peptide that binds to the BH4 domain, blocking Bcl-2-IP3R interaction and thus inducing Ca2+-mediated apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, multiple myeloma, and follicular lymphoma cells, including cells resistant to ABT-263, ABT-199, or the Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor Ibrutinib. Moreover, combining BIRD-2 with ABT-263 or ABT-199 enhances apoptosis induction compared to single agent treatment. Overall, these findings provide strong rationale for developing novel therapeutic agents that mimic the action of BIRD-2 in targeting the BH4 domain of Bcl-2 and disrupting Bcl-2-IP3R interaction.
Keywords: ABT-199; Bcl-2; Bruton's tyrosine kinase; inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor; lymphoid malignancy.
Conflict of interest statement
CWD is issued Patent US 8,034,779 B2 “Inhibitors of BCL-2” covering the use of the peptide referred to herein as BIRD-2 and targeting Bcl-2-IP3R interaction for cancer treatment.
Figures



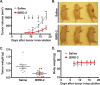
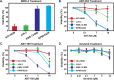
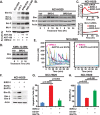



Similar articles
-
A dual role for the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein in cancer: mitochondria versus endoplasmic reticulum.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Oct;1843(10):2240-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.04.017. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24768714 Review.
-
Targeting Bcl-2-IP3 receptor interaction to treat cancer: A novel approach inspired by nearly a century treating cancer with adrenal corticosteroid hormones.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018 Nov;1865(11 Pt B):1795-1804. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.07.020. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 30053503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The trans-membrane domain of Bcl-2α, but not its hydrophobic cleft, is a critical determinant for efficient IP3 receptor inhibition.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 23;7(34):55704-55720. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11005. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27494888 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Bcl-2 based on the interaction of its BH4 domain with the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jun;1793(6):971-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.10.015. Epub 2008 Nov 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19056433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic killing of human small cell lung cancer cells by the Bcl-2-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor disruptor BIRD-2 and the BH3-mimetic ABT-263.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Dec 31;6(12):e2034. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.355. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 26720343 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Creating a New Cancer Therapeutic Agent by Targeting the Interaction between Bcl-2 and IP3 Receptors.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019 Sep 3;11(9):a035196. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a035196. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019. PMID: 31110129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration of Ca2+ signaling regulates the breast tumor cell response to simvastatin and doxorubicin.Oncogene. 2018 Sep;37(36):4979-4993. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0329-6. Epub 2018 May 23. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29795329
-
Bcl-2 proteins and calcium signaling: complexity beneath the surface.Oncogene. 2016 Sep 29;35(39):5079-92. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.31. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26973249 Review.
-
Inhibition of InsP3R with Xestospongin B Reduces Mitochondrial Respiration and Induces Selective Cell Death in T Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 11;22(2):651. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020651. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33440859 Free PMC article.
-
The BCL2 family: from apoptosis mechanisms to new advances in targeted therapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Mar 21;10(1):91. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02176-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40113751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yip KW, Reed JC. Bcl-2 family proteins and cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27:6398–6406. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
-
- Youle RJ, Strasser A. The Bcl-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:47–59. - PubMed
-
- Tse C, Shoemaker AR, Adickes J, Anderson MG, Chen J, Jin S, Johnson EF, Marsh KC, Mitten MJ, Nimmer P, Roberts L, Tahir SK, Xiao Y, Yang X, Zhang H, Fesik S, et al. ABT-263: A potent and orally bioavailable Bcl-2 family inhibitor. Cancer Res. 2008;68:3421–3328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

