Molecular Markers of Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Cell Damage in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 26317775
- PMCID: PMC4552842
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136994
Molecular Markers of Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Cell Damage in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
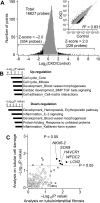
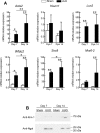
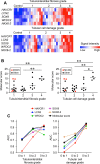
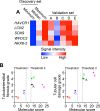
In chronic kidney disease (CKD), progressive nephron loss causes glomerular sclerosis, as well as tubulointerstitial fibrosis and progressive tubular injury. In this study, we aimed to identify molecular changes that reflected the histopathological progression of renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis and tubular cell damage. A discovery set of renal biopsies were obtained from 48 patients with histopathologically confirmed CKD, and gene expression profiles were determined by microarray analysis. The results indicated that hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 1 (also known as Kidney Injury Molecule-1, KIM-1), lipocalin 2 (also known as neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, NGAL), SRY-box 9, WAP four-disulfide core domain 2, and NK6 homeobox 2 were differentially expressed in CKD. Their expression levels correlated with the extent of tubulointerstitial fibrosis and tubular cell injury, determined by histopathological examination. The expression of these 5 genes was also increased as kidney damage progressed in a rodent unilateral ureteral obstruction model of CKD. We calculated a molecular score using the microarray gene expression profiles of the biopsy specimens. The composite area under the receiver operating characteristics curve plotted using this molecular score showed a high accuracy for diagnosing tubulointerstitial fibrosis and tubular cell damage. The robust sensitivity of this score was confirmed in a validation set of 5 individuals with CKD. These findings identified novel molecular markers with the potential to contribute to the detection of tubular cell damage and tubulointerstitial fibrosis in the kidney.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Nath KA. Tubulointerstitial changes as a major determinant in the progression of renal damage. Am J Kidney Dis. 1992;20(1):1–17. . - PubMed
-
- Mishra J, Ma Q, Prada A, Mitsnefes M, Zahedi K, Yang J, et al. Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14(10):2534–43. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

