Resolvins Decrease Oxidative Stress Mediated Macrophage and Epithelial Cell Interaction through Decreased Cytokine Secretion
- PMID: 26317859
- PMCID: PMC4552682
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136755
Resolvins Decrease Oxidative Stress Mediated Macrophage and Epithelial Cell Interaction through Decreased Cytokine Secretion
Abstract
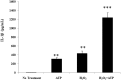
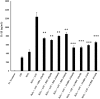
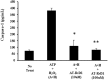
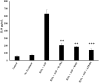
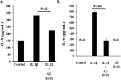
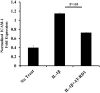
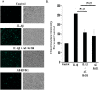
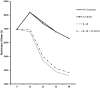
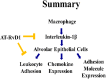
Background: Inflammation is a key hallmark of ALI and is mediated through ungoverned cytokine signaling. One such cytokine, interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) has been demonstrated to be the most bioactive cytokine in ALI patients. Macrophages are the key players responsible for IL-1β secretion into the alveolar space. Following the binding of IL-1β to its receptor, "activated" alveolar epithelial cells show enhanced barrier dysfunction, adhesion molecule expression, cytokine secretion, and leukocyte attachment. More importantly, it is an important communication molecule between the macrophage and alveolar epithelium. While the molecular determinants of this inflammatory event have been well documented, endogenous resolution processes that decrease IL-1β secretion and resolve alveolar epithelial cell activation and tissue inflammation have not been well characterized. Lipid mediator Aspirin-Triggered Resolvin D1 (AT-RvD1) has demonstrated potent pro-resolutionary effects in vivo models of lung injury; however, the contribution of the alveoli to the protective benefits of this molecule has not been well documented. In this study, we demonstrate that AT-RvD1 treatment lead to a significant decrease in oxidant induced macrophage IL-1β secretion and production, IL-1β-mediated cytokine secretion, adhesion molecule expression, leukocyte adhesion and inflammatory signaling.
Methods: THP-1 macrophages were treated with hydrogen peroxide and extracellular ATP in the presence or absence of AT-RvD1 (1000-0.1 nM). A549 alveolar-like epithelial cells were treated with IL-1β (10 ng/mL) in the presence or absence of AT-RvD1 (0.1 μM). Following treatment, cell lysate and cell culture supernatants were collected for Western blot, qPCR and ELISA analysis of pro-inflammatory molecules. Functional consequences of IL-1β induced alveolar epithelial cell and macrophage activation were also measured following treatment with IL-1β ± AT-RvD1.
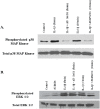
Results: Results demonstrate that macrophages exposed to H2O2 and ATP in the presence of resolvins show decreased IL-1β production and activity. A549 cells treated with IL-1β in the presence of AT-RvD1 show a reduced level of proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-8. Further, IL-1β-mediated adhesion molecule expression was also reduced with AT-RvD1 treatment, which was correlated with decreased leukocyte adhesion. AT-RvD1 treatment demonstrated reduced MAP-Kinase signaling. Taken together, our results demonstrate AT-RvD1 treatment reduced IL-1β-mediated alveolar epithelial cell activation. This is a key step in unraveling the protective effects of resolvins, especially AT-RvD1, during injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 reduces mucosal inflammation and promotes resolution in a murine model of acute lung injury.Mucosal Immunol. 2013 Mar;6(2):256-66. doi: 10.1038/mi.2012.66. Epub 2012 Jul 11. Mucosal Immunol. 2013. PMID: 22785226 Free PMC article.
-
Resolvin D1-mediated NOX2 inactivation rescues macrophages undertaking efferocytosis from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Sep 15;86(6):759-69. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23856291
-
Resolvin D1 stimulates alveolar fluid clearance through alveolar epithelial sodium channel, Na,K-ATPase via ALX/cAMP/PI3K pathway in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury.J Immunol. 2014 Apr 15;192(8):3765-77. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302421. Epub 2014 Mar 19. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24646745
-
Acute Lung Injury: IL-17A-Mediated Inflammatory Pathway and Its Regulation by Curcumin.Inflammation. 2019 Aug;42(4):1160-1169. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01010-4. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 31011925 Review.
-
Resolvin D1: A key endogenous inhibitor of neuroinflammation.Biofactors. 2022 Sep;48(5):1005-1026. doi: 10.1002/biof.1891. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Biofactors. 2022. PMID: 36176016 Review.
Cited by
-
Resolvin D1 Promotes SIRT1 Expression to Counteract the Activation of STAT3 and NF-κB in Mice with Septic-Associated Lung Injury.Inflammation. 2018 Oct;41(5):1762-1771. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0819-2. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 30014231
-
ROS/TNF-α Crosstalk Triggers the Expression of IL-8 and MCP-1 in Human Monocytic THP-1 Cells via the NF-κB and ERK1/2 Mediated Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 29;22(19):10519. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910519. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638857 Free PMC article.
-
Specialized Pro-resolving Mediators Regulate Alveolar Fluid Clearance during Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Apr 20;131(8):982-989. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.229890. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018. PMID: 29664060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial Cells Attenuate Toll-Like Receptor-Mediated Inflammatory Responses in Monocyte-Derived Macrophage-Like Cells to Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Modulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Sep 26;2018:3685948. doi: 10.1155/2018/3685948. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 30356420 Free PMC article.
-
BMI1 Silencing Induces Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Lung Epithelial Cells Exposed to Hyperoxia.Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 30;13:814510. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.814510. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35431986 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matthay MA, Zimmerman GA. Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: four decades of inquiry into pathogenesis and rational management. American journal of respiratory cell and molecular biology. 2005;33(4):319–27. Epub 2005/09/21. 10.1165/rcmb.F305 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPmc2715340. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

