Hypertonic Saline Dextran Ameliorates Organ Damage in Beagle Hemorrhagic Shock
- PMID: 26317867
- PMCID: PMC4552817
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136012
Hypertonic Saline Dextran Ameliorates Organ Damage in Beagle Hemorrhagic Shock
Abstract
Objective: The goal of this study was to investigate the effect of hypertonic saline with 6% Dextran-70 (HSD) resuscitation on organ damage and the resuscitation efficiency of the combination of HSD and lactated ringers (LR) in a model of hemorrhage shock in dogs.
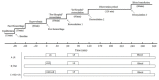
Methods: Beagles were bled to hold their mean arterial pressure (MAP) at 50 ± 5 mmHg for 1 h. After hemorrhage, beagles were divided into three groups (n = 7) to receive pre-hospital resuscitation for 1 h (R1): HSD (4 ml/kg), LR (40 ml/kg), and HSD+LR (a combination of 4 ml/kg HSD and 40 ml/kg LR). Next, LR was transfused into all groups as in-hospital resuscitation (R2). After two hours of observation (R3), autologous blood was transfused. Hemodynamic responses and systemic oxygenation were measured at predetermined phases. Three days after resuscitation, the animals were sacrificed and tissues including kidney, lung, liver and intestinal were obtained for pathological analysis.
Results: Although the initial resuscitation with HSD was shown to be faster than LR with regard to an ascending MAP, the HSD group showed a similar hemodynamic performance compared to the LR group throughout the experiment. Compared with the LR group, the systemic oxygenation performance in the HSD group was similar but showed a lower venous-to-arterial CO2 gradient (Pv-aCO2) at R3 (p < 0.05). Additionally, the histology score of the kidneys, lungs and liver were significantly lower in the HSD group than in the LR group (p < 0.05). The HSD+LR group showed a superior hemodynamic response but higher extravascular lung water (EVLW) and lower arterial oxygen tension (PaO2) than the other groups (p < 0.05). The HSD+LR group showed a marginally improved systemic oxygenation performance and lower histology score than other groups.
Conclusions: Resuscitation after hemorrhagic shock with a bolus of HSD showed a similar hemodynamic response compared with LR at ten times the volume of HSD, but HSD showed superior efficacy in organ protection. Our findings suggest that resuscitation with the combination of HSD and LR in the pre-hospital setting is an effective treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Wade CE, Dubick MA, Vassar MJ, Perry CA, Holcroft JW (1996) Plasma dextran concentrations in trauma patients administered hypertonic saline-dextran-70. Clin Chem 42:779–780. - PubMed
-
- Riddez L, Stahlberg H, Suneson A, Hjelmqvist H (2001) Early resuscitation with hypertonic saline/dextran in uncontrolled intra-abdominal bleeding in swine combined with a soft tissue gunshot wound. Mil Med 166:695–699. - PubMed
-
- Bickell WH, Bruttig SP, Millnamow GA, O'Benar J, Wade CE (1992) Use of hypertonic saline/ dextran versus lactated Ringer's solution as a resuscitation fluid after uncontrolled aortic hemorrhage in anesthetized swine. Ann Emerg Med 21:1077–1085. - PubMed
-
- Vassar MJ, Perry CA, Gannaway WL, Holcroft JW (1991) 7.5% sodium chloride/dextran for resuscitation of trauma patients undergoing helicopter transport. Arch Surg 126: 1065–1072. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

