High-content assays for characterizing the viability and morphology of 3D cancer spheroid cultures
- PMID: 26317884
- PMCID: PMC4556086
- DOI: 10.1089/adt.2015.655
High-content assays for characterizing the viability and morphology of 3D cancer spheroid cultures
Abstract
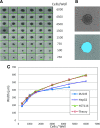
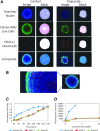
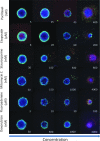
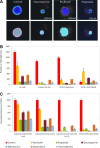
There is an increasing interest in using three-dimensional (3D) spheroids for modeling cancer and tissue biology to accelerate translation research. Development of higher throughput assays to quantify phenotypic changes in spheroids is an active area of investigation. The goal of this study was to develop higher throughput high-content imaging and analysis methods to characterize phenotypic changes in human cancer spheroids in response to compound treatment. We optimized spheroid cell culture protocols using low adhesion U-bottom 96- and 384-well plates for three common cancer cell lines and improved the workflow with a one-step staining procedure that reduces assay time and minimizes variability. We streamlined imaging acquisition by using a maximum projection algorithm that combines cellular information from multiple slices through a 3D object into a single image, enabling efficient comparison of different spheroid phenotypes. A custom image analysis method was implemented to provide multiparametric characterization of single-cell and spheroid phenotypes. We report a number of readouts, including quantification of marker-specific cell numbers, measurement of cell viability and apoptosis, and characterization of spheroid size and shape. Assay performance was assessed using established anticancer cytostatic and cytotoxic drugs. We demonstrated concentration-response effects for different readouts and measured IC50 values, comparing 3D spheroid results to two-dimensional cell cultures. Finally, a library of 119 approved anticancer drugs was screened across a wide range of concentrations using HCT116 colon cancer spheroids. The proposed methods can increase performance and throughput of high-content assays for compound screening and evaluation of anticancer drugs with 3D cell models.
Figures



References
-
- Kunz-Schughart LA, Freyer JP, Hofstaedter F, et al. : The use of 3-D cultures for high-throughput screening: the multicellular spheroid model. J Biomol Screen 2004;9:273–285 - PubMed
-
- Mueller-Klieser W. Three-dimensional cell cultures: from molecular mechanisms to clinical applications. Am J Physiol 1997;273:C1109–C1123 - PubMed
-
- Wartenberg M, Donmez F, Ling FC, et al. : Tumor-induced angiogenesis studied in confrontation cultures of multicellular tumor spheroids and embryoid bodies grown from pluripotent embryonic stem cells. FASEB J 2001;15:995–1005 - PubMed
-
- Frieboes HB, Zheng X, Sun CH, et al. : An integrated computational/experimental model of tumor invasion. Cancer Res 2006;66:1597–1604 - PubMed
-
- Wenzel C, Riefke B, Grundemann S, et al. : 3D high-content screening for the identification of compounds that target cells in dormant tumor spheroid regions. Exp Cell Res 2014;323:131–143 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
