Combinatorial high-throughput experimental and bioinformatic approach identifies molecular pathways linked with the sensitivity to anticancer target drugs
- PMID: 26317900
- PMCID: PMC4694985
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4507
Combinatorial high-throughput experimental and bioinformatic approach identifies molecular pathways linked with the sensitivity to anticancer target drugs
Abstract
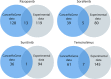
Effective choice of anticancer drugs is important problem of modern medicine. We developed a method termed OncoFinder for the analysis of new type of biomarkers reflecting activation of intracellular signaling and metabolic molecular pathways. These biomarkers may be linked with the sensitivity to anticancer drugs. In this study, we compared the experimental data obtained in our laboratory and in the Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer (GDS) project for testing response to anticancer drugs and transcriptomes of various human cell lines. The microarray-based profiling of transcriptomes was performed for the cell lines before the addition of drugs to the medium, and experimental growth inhibition curves were built for each drug, featuring characteristic IC50 values. We assayed here four target drugs - Pazopanib, Sorafenib, Sunitinib and Temsirolimus, and 238 different cell lines, of which 11 were profiled in our laboratory and 227 - in GDS project. Using the OncoFinder-processed transcriptomic data on ~600 molecular pathways, we identified pathways showing significant correlation between pathway activation strength (PAS) and IC50 values for these drugs. Correlations reflect relationships between response to drug and pathway activation features. We intersected the results and found molecular pathways significantly correlated in both our assay and GDS project. For most of these pathways, we generated molecular models of their interaction with known molecular target(s) of the respective drugs. For the first time, our study uncovered mechanisms underlying cancer cell response to drugs at the high-throughput molecular interactomic level.
Keywords: anticancer target drugs; cancer; gene expression; metabolic pathway; signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bioinformatics Meets Biomedicine: OncoFinder, a Quantitative Approach for Interrogating Molecular Pathways Using Gene Expression Data.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1613:53-83. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7027-8_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28849558
-
Molecular analysis of sunitinib resistant renal cell carcinoma cells after sequential treatment with RAD001 (everolimus) or sorafenib.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 Feb;19(2):430-41. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12471. Epub 2014 Dec 2. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25444514 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome profiling in response to adiponectin in human cancer-derived cells.Physiol Genomics. 2010 Sep;42A(1):61-70. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00013.2010. Epub 2010 Jun 22. Physiol Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20571111
-
Clinical management of metastatic kidney cancer: the role of new molecular drugs.Future Oncol. 2016 Jan;12(1):83-93. doi: 10.2217/fon.15.283. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Future Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26617188 Review.
-
An update on targeted therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Urol Oncol. 2012 May-Jun;30(3):240-6. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2009.12.018. Epub 2010 Apr 24. Urol Oncol. 2012. PMID: 20456985 Review.
Cited by
-
Algorithmically Reconstructed Molecular Pathways as the New Generation of Prognostic Molecular Biomarkers in Human Solid Cancers.Proteomes. 2023 Aug 25;11(3):26. doi: 10.3390/proteomes11030026. Proteomes. 2023. PMID: 37755705 Free PMC article.
-
Intratumoral Heterogeneity and Longitudinal Changes in Gene Expression Predict Differential Drug Sensitivity in Newly Diagnosed and Recurrent Glioblastoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Feb 24;12(2):520. doi: 10.3390/cancers12020520. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32102350 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Sequencing-Based Identification of Ganglioside GD2-Positive Cancer Phenotype.Biomedicines. 2020 May 30;8(6):142. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8060142. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32486168 Free PMC article.
-
Green One-Pot Synthesis of Thiazole Scaffolds Catalyzed by Reusable NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles: In Silico Binding Affinity and In Vitro Anticancer Activity Studies.ACS Omega. 2024 Aug 29;9(36):38262-38271. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c05587. eCollection 2024 Sep 10. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39281943 Free PMC article.
-
Enterotoxins A and B produced by Staphylococcus aureus increase cell proliferation, invasion and cytarabine resistance in acute myeloid leukemia cell lines.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 2;9(9):e19743. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19743. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37810000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rochat B. Importance of influx and efflux systems and xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in intratumoral disposition of anticancer agents. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2009;5:652–764. - PubMed
-
- Rafii A, Touboul C, Al Thani H, Suhre K, Malek JA. Where cancer genomics should go next: a clinician's perspective. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23:R69–75. - PubMed
-
- Iyer G, Hanrahan AJ, Milowsky MI, Al-Ahmadie H, Scott SN, Janakiraman M, Pirun M, Sander C, Socci ND, Ostrovnaya I, Viale A, Heguy A, Peng L, Chan TA, Bochner B, Bajorin DF, Berger MF, Taylor BS, Solit DB. Genome sequencing identifies a basis for everolimus sensitivity. Science. 2012;338:221. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shoemaker RH. The NCI60 human tumour cell line anticancer drug screen. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:813–23. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

