Bortezomib inhibits Burkitt's lymphoma cell proliferation by downregulating sumoylated hnRNP K and c-Myc expression
- PMID: 26317903
- PMCID: PMC4694880
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4620
Bortezomib inhibits Burkitt's lymphoma cell proliferation by downregulating sumoylated hnRNP K and c-Myc expression
Abstract
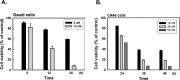
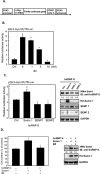
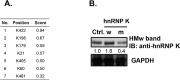
Bortezomib (Velcal) was the first proteasome inhibitor to be approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myelomas. Previous studies have demonstrated that bortezomib inhibits tumor cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by blocking the nuclear factor (NF)-κB pathway. However, the exact mechanism by which bortezomib induces cancer cell apoptosis is still not well understood. In this study, we found that bortezomib significantly inhibited cell proliferation in both human Burkitt's lymphoma CA46 and Daudi cells. Through proteomic analysis, we found that bortezomib treatment changed the expression of various proteins in distinct functional categories including unfolding protein response (UPS), RNA processing, protein targeting and biosynthesis, apoptosis, and signal transduction. Among the proteins with altered expression, hnRNP K, hnRNP H, Hsp90α, Grp78, and Hsp7C were common to both Daudi and CA46 cells. Interestingly, bortezomib treatment downregulated the expression of high-molecular-weight (HMw) hnRNP K and c-Myc but upregulated the expression of low-molecular-weight (LMw) hnRNP K. Moreover, cell proliferation was significantly correlated with high expression of HMw hnRNP K and c-Myc. HMw and LMw hnRNP K were identified as sumoylated and desumoylated hnRNP K, respectively. Using transient transfection, we found that sumoylated hnRNP K increased c-Myc expression at the translational level and contributed to cell proliferation, and that Lys422 of hnRNP K is the candidate sumoylated residue. Our results suggest that besides inhibiting the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, bortezomib may inhibit cell proliferation by downregulating sumoylated hnRNP K and c-Myc expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cells.
Keywords: Bortezomib; Burkitt’s lymphoma; c-Myc; hnRNP K; sumoylation.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




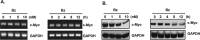
References
-
- Hamrick-Turner JE, Saif MF, Powers CI, Blumenthal BI, Royal SA, Iyer RV. Imaging of childhood non-Hodgkin lymphoma: assessment by histologic subtype. Radiographics. 1994;14:11–28. - PubMed
-
- Magrath I. Epidemiology: clues to the pathogenesis of Burkitt lymphoma. Brit J Haematol. 2012;156:744–756. - PubMed
-
- Molyneux EM, Rochford R, Griffin B, Newton R, Jackson G, Menon G, Harrison CJ, Israels T, Bailey S. Burkitt's lymphoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1234–1244. - PubMed
-
- Tomita N. BCL2 and MYC dual-hit lymphoma/leukemia. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2011;51:7–12. - PubMed
-
- Kenkre VP, Stock W. Burkitt lymphoma/leukemia: improving prognosis. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma. 2009;9:S231–S238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

