Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression
- PMID: 2631796
- PMCID: PMC1360503
Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression
Abstract
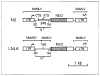
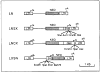
We describe a set of murine retrovirus-based vectors that include unique cloning sites for insertion of cDNAs such that the cDNA can be driven by either the retroviral long terminal repeat, the immediate early promoter of human cytomegalovirus, or the simian virus 40 early promoter. The vectors carry the neomycin phosphotransferase gene expressed from an alternate promoter as a selectable marker. These vectors have been constructed to prevent viral protein synthesis from the remaining viral sequences, to yield high-titer virus stocks after introduction into retrovirus packaging cells, and to eliminate homologous overlap with viral DNAs present in retrovirus packaging cells in order to prevent helper virus production. Methods for generating high-titer virus are described.
Figures

References
-
- Beck E, Ludwig G, Auerswald EA, Reiss B, Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene. 1982;19:327–336. - PubMed
-
- Boshart M, Weber F, Jahn G, Dorsch-Hsler K, Fleckenstein B, Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985;41:521–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
