Gender Determinants of Vaccination Status in Children: Evidence from a Meta-Ethnographic Systematic Review
- PMID: 26317975
- PMCID: PMC4552892
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135222
Gender Determinants of Vaccination Status in Children: Evidence from a Meta-Ethnographic Systematic Review
Abstract
Using meta-ethnographic methods, we conducted a systematic review of qualitative research to understand gender-related reasons at individual, family, community and health facility levels why millions of children in low and middle income countries are still not reached by routine vaccination programmes. A systematic search of Medline, Embase, CINAHL, Cochrane Library, ERIC, Anthropological Lit, CSA databases, IBSS, ISI Web of Knowledge, JSTOR, Soc Index and Sociological Abstracts was conducted. Key words were built around the themes of immunization, vaccines, health services, health behaviour, and developing countries. Only papers, which reported on in-depth qualitative data, were retained. Twenty-five qualitative studies, which investigated barriers to routine immunisation, were included in the review. These studies were conducted between 1982 and 2012; eighteen were published after 2000. The studies represent a wide range of low- to middle income countries including some that have well known coverage challenges. We found that women's low social status manifests on every level as a barrier to accessing vaccinations: access to education, income, as well as autonomous decision-making about time and resource allocation were evident barriers. Indirectly, women's lower status made them vulnerable to blame and shame in case of childhood illness, partly reinforcing access problems, but partly increasing women's motivation to use every means to keep their children healthy. Yet in settings where gender discrimination exists most strongly, increasing availability and information may not be enough to reach the under immunised. Programmes must actively be designed to include mitigation measures to facilitate women's access to immunisation services if we hope to improve immunisation coverage. Gender inequality needs to be addressed on structural, community and household levels if the number of unvaccinated children is to substantially decrease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

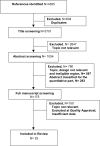

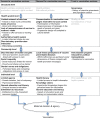
References
-
- WHO/UNICEF. WHO/UNICEF coverage estimates 2011 revision. July 2012. 2012.
-
- Centers for Disease Control. Global routine vaccination coverage, 2010. MMWR Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 2011;60(44):1520–1522. - PubMed
-
- Bosch-Capblanch X, Banerjee K, Burton A. Unvaccinated children in years of increasing coverage: how many and who are they? Evidence from 96 low- and middle-income countries. Tropical Medicine & International Health. 2012;17(6):697–710. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Meeting of the immunisation Strategic Advisory Group of Experts, November 2007. Conclusions and recommendations. Weekly Epidemiological Record. 2008;(1):1–16. - PubMed
-
- Lewin S, Hill S, Abdullahi LH, de Castro Freire SB, Bosch-Capblanch X, Glenton C, et al. 'Communicate to vaccinate' (COMMVAC). Building evidence for improving communication about childhood vaccinations in low- and middle-income countries: Protocol for a programme of research. Implementation Science. 2011;6:125 10.1186/1748-5908-6-125 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

