Structural Analysis of the Regulatory Domain of ExsA, a Key Transcriptional Regulator of the Type Three Secretion System in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 26317977
- PMCID: PMC4552939
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136533
Structural Analysis of the Regulatory Domain of ExsA, a Key Transcriptional Regulator of the Type Three Secretion System in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
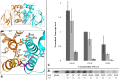
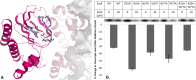
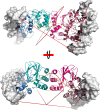
Pseudomonas aeruginosa employs a type three secretion system to facilitate infections in mammalian hosts. The operons encoding genes of structural components of the secretion machinery and associated virulence factors are all under the control of the AraC-type transcriptional activator protein, ExsA. ExsA belongs to a unique subfamily of AraC-proteins that is regulated through protein-protein contacts rather than small molecule ligands. Prior to infection, ExsA is inhibited through a direct interaction with the anti-activator ExsD. To activate ExsA upon host cell contact this interaction is disrupted by the anti-antiactivator protein ExsC. Here we report the crystal structure of the regulatory domain of ExsA, which is known to mediate ExsA dimerization as well as ExsD binding. The crystal structure suggests two models for the ExsA dimer. Both models confirmed the previously shown involvement of helix α-3 in ExsA dimerization but one also suggest a role for helix α-2. These structural data are supported by the observation that a mutation in α-2 greatly diminished the ability of ExsA to activate transcription in vitro. Additional in vitro transcription studies revealed that a conserved pocket, used by AraC and the related ToxT protein for the binding of small molecule regulators, although present in ExsA is not involved in binding of ExsD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

