Investigation of the role of βarrestin2 in kappa opioid receptor modulation in a mouse model of pruritus
- PMID: 26318102
- PMCID: PMC4739521
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.08.027
Investigation of the role of βarrestin2 in kappa opioid receptor modulation in a mouse model of pruritus
Abstract
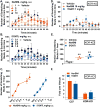
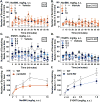
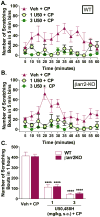
The kappa opioid receptor (KOR) is involved in mediating pruritus; agonists targeting this receptor have been used to treat chronic intractable itch. Conversely, antagonists induce an itch response at the site of injection. As a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), the KOR has potential for signaling via G proteins and βarrestins, however, it is not clear which of these pathways are involved in the KOR modulation of itch. In this study asked whether the actions of KOR in pruritus involve βarrestins by using βarrestin2 knockout (βarr2-KO) mice as well as a recently described biased KOR agonist that biases receptor signaling toward G protein pathways over βarrestin2 recruitment. We find that the KOR antagonists nor-binaltorphimine (NorBNI) and 5'-guanidinonaltrindole (5'GNTI) induce acute pruritus in C57BL/6J mice, with reduced effects in KOR-KO mice. βArr2-KO mice display less of a response to KOR antagonist-induced itch compared to wild types, however no genotype differences are observed from chloroquine phosphate (CP)-induced itch, suggesting that the antagonists may utilize a KOR-βarrestin2 dependent mechanism. The KOR agonist U50,488H was equally effective in both WT and βarr2-KO mice in suppressing CP-induced itch. Furthermore, the G protein biased agonist, Isoquinolinone 2.1 was as effective as U50,488H in suppressing the itch response induced by KOR antagonist NorBNI or CP in C57BL/6J mice. Together these data suggest that the antipruritic effects of KOR agonists may not require βarrestins.
Keywords: Biased ligand; KOR antagonist; Kappa opioid receptor; Mouse models of itch; Pruritus; U50,488H.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Quantification of observable behaviors induced by typical and atypical kappa-opioid receptor agonists in male rhesus monkeys.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020 Jul;237(7):2075-2087. doi: 10.1007/s00213-020-05519-7. Epub 2020 May 6. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32372348 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of kappa opioid receptor mediated, dynorphin-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding in mouse striatum for the evaluation of selective KOR ligands in an endogenous setting.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Dec;99:131-41. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.07.001. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 26160155 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoproteomic approach for agonist-specific signaling in mouse brains: mTOR pathway is involved in κ opioid aversion.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019 Apr;44(5):939-949. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0155-0. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30082888 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic kappa opioid receptor agonists in the treatment of chronic pruritus: a literature review.Acta Derm Venereol. 2012 Sep;92(5):555-60. doi: 10.2340/00015555-1353. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012. PMID: 22504709 Review.
-
Targeting Itch with Ligands Selective for κ Opioid Receptors.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2015;226:291-314. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-44605-8_16. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25861786 Review.
Cited by
-
β-Arrestins: Structure, Function, Physiology, and Pharmacological Perspectives.Pharmacol Rev. 2023 Sep;75(5):854-884. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.121.000302. Epub 2023 Apr 7. Pharmacol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37028945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of serotonin transporter function by kappa-opioid receptor ligands.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Feb;113(Pt A):281-292. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.10.011. Epub 2016 Oct 12. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 27743931 Free PMC article.
-
IUPHAR themed review: Opioid efficacy, bias, and selectivity.Pharmacol Res. 2023 Nov;197:106961. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106961. Epub 2023 Oct 14. Pharmacol Res. 2023. PMID: 37844653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of β-arrestin 2 in mice affects kappa opioid receptor-mediated behaviors depending on sex, ovariectomy status, and behavioral endpoints.Neurosci Lett. 2025 Feb 28;850:138154. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2025.138154. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Neurosci Lett. 2025. PMID: 39923977
-
Fundamentals of the Dynorphins/Kappa Opioid Receptor System: From Distribution to Signaling and Function.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022;271:3-21. doi: 10.1007/164_2021_433. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 33754230 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bohn LM, Lefkowitz RJ, Gainetdinov RR, Peppel K, Caron MG, Lin FT. Enhanced morphine analgesia in mice lacking beta-arrestin 2. Science. 1999;286:2495–2498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

