A randomised, double-blind, phase III study comparing SB2, an infliximab biosimilar, to the infliximab reference product Remicade in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate therapy
- PMID: 26318384
- PMCID: PMC5264229
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207764
A randomised, double-blind, phase III study comparing SB2, an infliximab biosimilar, to the infliximab reference product Remicade in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate therapy
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the efficacy, safety, immunogenicity and pharmacokinetics (PK) of SB2 to the infliximab reference product (INF) in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA) despite methotrexate therapy.
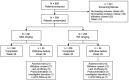
Methods: This is a phase III, randomised, double-blind, multinational, multicentre parallel group study. Patients with moderate to severe RA despite methotrexate therapy were randomised in a 1:1 ratio to receive either SB2 or INF of 3 mg/kg. The primary end point was the American College of Rheumatology 20% (ACR20) response at week 30. Inclusion of the 95% CI of the ACR20 response difference within a ±15% margin was required for equivalence.
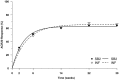
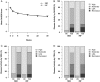
Results: 584 subjects were randomised into SB2 (N=291; 290 analysed) or INF (N=293). The ACR20 response at week 30 in the per-protocol set was 64.1% in SB2 versus 66.0% in INF. The adjusted rate difference was -1.88% (95% CI -10.26% to 6.51%), which was within the predefined equivalence margin. Other efficacy outcomes such as ACR50/70, disease activity score measured by 28 joints and European League against Rheumatism response were similar between SB2 and INF. The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events was comparable (57.6% in SB2 vs 58.0% in INF) as well as the incidence of antidrug antibodies (ADA) to infliximab up to week 30 (55.1% in SB2 vs 49.7% in INF). The PK profile was similar between SB2 and INF. Efficacy, safety and PK by ADA subgroup were comparable between SB2 and INF.
Conclusions: SB2 was equivalent to INF in terms of ACR20 response at week 30. SB2 was well tolerated with a comparable safety profile, immunogenicity and PK to INF.
Trial registration number: NCT01936181.
Keywords: Anti-TNF; DMARDs (biologic); Disease Activity; Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/.
Conflict of interest statement
J-YC reports receiving grant/research support and consultant fees from Samsung Bioepis. JSS reports receiving grant/research support from AbbVie, Jassen, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, UCB, Consultant for: AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Astro-Pharma, Celgene, GSK, Jassen, Lilly, Medimmune, MSD, Norvartis-Sandoz, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi, UCB. AB reports receiving grant/research support from AbbVie and Samsung Bioepis. NP, JN, IS, ED, RY, MM, WP, HC, KJ-R and AZ report receiving grant/research support from Samsung Bioepis. JC and YHR are employees of Samsung Bioepis.
Figures

Comment in
-
Clinical trials of biosimilars should become more similar.Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Jan;76(1):4-6. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208113. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 27566795 No abstract available.
References
-
- Maini R, St Clair EW, Breedveld F, et al. . Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomised phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet 1999;354:1932–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

