Diversity in the structures and ligand-binding sites of nematode fatty acid and retinol-binding proteins revealed by Na-FAR-1 from Necator americanus
- PMID: 26318523
- PMCID: PMC4613501
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20150068
Diversity in the structures and ligand-binding sites of nematode fatty acid and retinol-binding proteins revealed by Na-FAR-1 from Necator americanus
Abstract
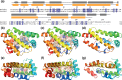
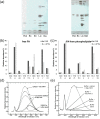
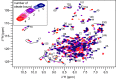
Fatty acid and retinol-binding proteins (FARs) comprise a family of unusual α-helix rich lipid-binding proteins found exclusively in nematodes. They are secreted into host tissues by parasites of plants, animals and humans. The structure of a FAR protein from the free-living nematode Caenorhabditis elegans is available, but this protein [C. elegans FAR-7 (Ce-FAR-7)] is from a subfamily of FARs that does not appear to be important at the host/parasite interface. We have therefore examined [Necator americanus FAR-1 (Na-FAR-1)] from the blood-feeding intestinal parasite of humans, N. americanus. The 3D structure of Na-FAR-1 in its ligand-free and ligand-bound forms, determined by NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography respectively, reveals an α-helical fold similar to Ce-FAR-7, but Na-FAR-1 possesses a larger and more complex internal ligand-binding cavity and an additional C-terminal α-helix. Titration of apo-Na-FAR-1 with oleic acid, analysed by NMR chemical shift perturbation, reveals that at least four distinct protein-ligand complexes can be formed. Na-FAR-1 and possibly other FARs may have a wider repertoire for hydrophobic ligand binding, as confirmed in the present study by our finding that a range of neutral and polar lipids co-purify with the bacterially expressed recombinant protein. Finally, we show by immunohistochemistry that Na-FAR-1 is present in adult worms with a tissue distribution indicative of possible roles in nutrient acquisition by the parasite and in reproduction in the male.
Keywords: Necator americanus; X-ray; fatty acid-binding protein; nematode; nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR); parasite; protein structure; retinol-binding protein.
© 2015 Authors; published by Portland Press Limited.
Figures


Similar articles
-
¹H, ¹³C and ¹⁵N chemical shift assignments of Na-FAR-1, a helix-rich fatty acid and retinol binding protein of the parasitic nematode Necator americanus.Biomol NMR Assign. 2014 Apr;8(1):19-21. doi: 10.1007/s12104-012-9444-4. Epub 2012 Nov 20. Biomol NMR Assign. 2014. PMID: 23179061 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty Acid and Retinol-Binding Protein: Unusual Protein Conformational and Cavity Changes Dictated by Ligand Fluctuations.J Chem Inf Model. 2019 Aug 26;59(8):3545-3555. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00364. Epub 2019 Aug 6. J Chem Inf Model. 2019. PMID: 31365253
-
Two crystal forms of a helix-rich fatty acid- and retinol-binding protein, Na-FAR-1, from the parasitic nematode Necator americanus.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2012 Jul 1;68(Pt 7):835-8. doi: 10.1107/S1744309112023597. Epub 2012 Jun 28. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2012. PMID: 22750878 Free PMC article.
-
Sterol carrier protein-2: structure reveals function.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002 Feb;59(2):193-212. doi: 10.1007/s00018-002-8416-8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002. PMID: 11915938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improved insights into the transcriptomes of the human hookworm Necator americanus--fundamental and biotechnological implications.Biotechnol Adv. 2009 Mar-Apr;27(2):122-32. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.10.002. Epub 2008 Oct 18. Biotechnol Adv. 2009. PMID: 18977428 Review.
Cited by
-
Fatty acid- and retinol-binding protein 6 does not control worm fatty acid content in Caenorhabditis elegans but might play a role in Haemonchus contortus parasitism.Parasit Vectors. 2023 Jul 10;16(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-05836-8. Parasit Vectors. 2023. PMID: 37430357 Free PMC article.
-
Nb-FAR-1: A key developmental protein affects lipid droplet accumulation and cuticle formation in Nippostrongylus brasiliensis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025 Jan 17;19(1):e0012769. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012769. eCollection 2025 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025. PMID: 39823413 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal Structure of Borrelia turicatae protein, BTA121, a differentially regulated gene in the tick-mammalian transmission cycle of relapsing fever spirochetes.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 10;7(1):15310. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14959-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29127407 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational changes, from β-strand to α-helix, of the fatty acid-binding protein ReP1-NCXSQ in anionic lipid membranes: dependence with the vesicle curvature.Eur Biophys J. 2018 Mar;47(2):165-177. doi: 10.1007/s00249-017-1243-5. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Eur Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 28752207
-
Structure and ligand binding of As-p18, an extracellular fatty acid binding protein from the eggs of a parasitic nematode.Biosci Rep. 2019 Jul 23;39(7):BSR20191292. doi: 10.1042/BSR20191292. Print 2019 Jul 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31273060 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meenan N.A, Ball G., Bromek K., Uhrin D., Cooper A., Kennedy M.W., Smith B.O. Solution structure of a repeated unit of the ABA-1 nematode polyprotein allergen of ascaris reveals a novel fold and two discrete lipid-binding sites. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011;5:e1040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001040. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

