Comparative analysis of multiple inducible phages from Mannheimia haemolytica
- PMID: 26318735
- PMCID: PMC4553209
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-015-0494-5
Comparative analysis of multiple inducible phages from Mannheimia haemolytica
Abstract
Background: Mannheimia haemolytica is a commensal bacterium that resides in the upper respiratory tract of cattle that can play a role in bovine respiratory disease. Prophages are common in the M. haemolytica genome and contribute significantly to host diversity. The objective of this research was to undertake comparative genomic analysis of phages induced from strains of M. haemolytica serotype A1 (535A and 2256A), A2 (587A and 1127A) and A6 (1152A and 3927A).
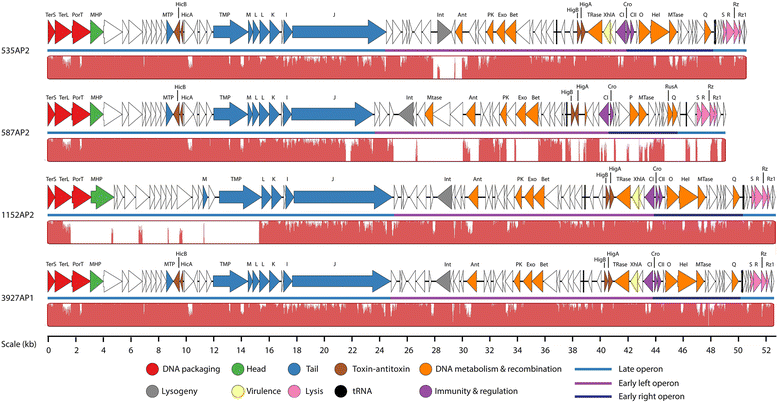
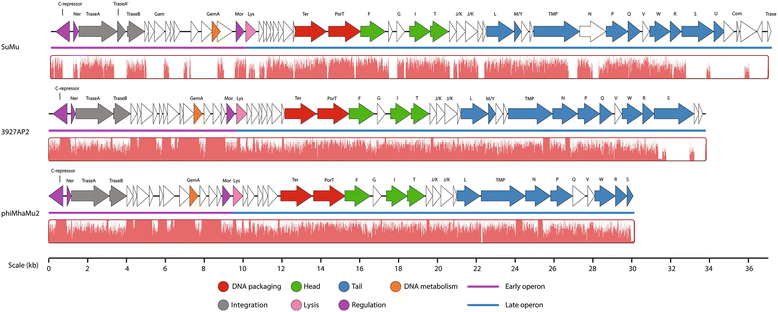
Results: Overall, four P2-like (535AP1, 587AP1, 1127AP1 and 2256AP1; genomes: 34.9-35.7 kb; G+C content: 41.5-42.1 %; genes: 51-53 coding sequences, CDSs), four λ-like (535AP2, 587AP2, 1152AP2 and 3927AP1; genomes: 48.6-52.1 kb; 41.1-41.4 % mol G+C; genes: 77-83 CDSs and 2 tRNAs) and one Mu-like (3927AP2; genome: 33.8 kb; 43.1 % mol G+C; encoding 50 CDSs) phages were identified. All P2-like phages are collinear with the temperate phage φMhaA1-PHL101 with 535AP1, 2256AP1 and 1152AP1 being most closely related, followed by 587AP1 and 1127AP1. Lambdoid phages are not collinear with any other known λ-type phages, with 587AP2 being distinct from 535AP2, 3927AP1 and 1152AP2. All λ-like phages contain genes encoding a toxin-antitoxin (TA) system and cell-associated haemolysin XhlA. The Mu-like phage induced from 3927A is closely related to the phage remnant φMhaMu2 from M. haemolytica PHL21, with similar Mu-like phages existing in the genomes of M. haemolytica 535A and 587A.
Conclusions: This is among the first reports of both λ- and Mu-type phages being induced from M. haemolytica. Compared to phages induced from commensal strains of M. haemolytica serotype A2, those induced from the more virulent A1 and A6 serotypes are more closely related. Moreover, when P2-, λ- and Mu-like phages co-existed in the M. haemolytica genome, only P2- and λ-like phages were detected upon induction, suggesting that Mu-type phages may be more resistant to induction. Toxin-antitoxin gene cassettes in λ-like phages may contribute to their genomic persistence or the establishment of persister subpopulations of M. haemolytica. Further work is required to determine if the cell-associated haemolysin XhlA encoded by λ-like phages contributes to the pathogenicity and ecological fitness of M. haemolytica.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Investigation of Mannheimia haemolytica bacteriophages relative to host diversity.J Appl Microbiol. 2013 Jun;114(6):1592-603. doi: 10.1111/jam.12185. Epub 2013 Apr 4. J Appl Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23489937
-
Diversity of temperate bacteriophages induced in bovine and ovine Mannheimia haemolytica isolates and identification of a new P2-like phage.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006 Jul;260(2):162-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00314.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006. PMID: 16842340
-
Complete nucleotide sequence of a P2 family lysogenic bacteriophage, varphiMhaA1-PHL101, from Mannheimia haemolytica serotype A1.Virology. 2006 Jun 20;350(1):79-89. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.03.024. Epub 2006 May 2. Virology. 2006. PMID: 16631219
-
[Mannheimia haemolytica and the pathogenesis of enzootic bronchopneumonia].Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2004 Mar-Apr;117(3-4):97-115. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2004. PMID: 15046457 Review. German.
-
Comparative genomics of phages and prophages in lactic acid bacteria.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2002 Aug;82(1-4):73-91. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2002. PMID: 12369206 Review.
Cited by
-
Diversity and characterization of temperate bacteriophages induced in Pasteurella multocida from different host species.BMC Microbiol. 2021 Mar 30;21(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02155-9. BMC Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33784980 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Genomics of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae Serotype 8 Reveals the Importance of Prophages in the Genetic Variability of the Species.Int J Genomics. 2020 Feb 18;2020:9354204. doi: 10.1155/2020/9354204. eCollection 2020. Int J Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32149072 Free PMC article.
-
Pasteurella multocida: Genotypes and Genomics.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2019 Sep 4;83(4):e00014-19. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00014-19. Print 2019 Nov 20. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2019. PMID: 31484691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic Analysis of Pasteurella atlantica Provides Insight on Its Virulence Factors and Phylogeny and Highlights the Potential of Reverse Vaccinology in Aquaculture.Microorganisms. 2021 Jun 4;9(6):1215. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9061215. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34199775 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing bacteriophage screening and isolation methods for microbial samples derived from different body sites of cattle.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 5:2025.07.04.663187. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.04.663187. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40631329 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

