Osteoprotegerin is an effective countermeasure for spaceflight-induced bone loss in mice
- PMID: 26318907
- PMCID: PMC7937349
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.08.021
Osteoprotegerin is an effective countermeasure for spaceflight-induced bone loss in mice
Abstract
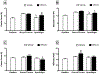
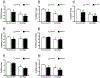
Bone loss associated with microgravity exposure poses a significant barrier to long-duration spaceflight. Osteoprotegerin-Fc (OPG-Fc) is a receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL) inhibitor that causes sustained inhibition of bone resorption after a single subcutaneous injection. We tested the ability of OPG-Fc to preserve bone mass during 12 days of spaceflight (SF). 64-day-old female C57BL/6J mice (n=12/group) were injected subcutaneously with OPG-Fc (20mg/kg) or an inert vehicle (VEH), 24h prior to launch. Ground control (GC) mice (VEH or OPG-Fc) were maintained under environmental conditions that mimicked those in the space shuttle middeck. Age-matched baseline (BL) controls were sacrificed at launch. GC/VEH, but not SF/VEH mice, gained tibia BMD and trabecular volume fraction (BV/TV) during the mission (P<0.05 vs. BL). SF/VEH mice had lower BV/TV vs. GC/VEH mice, while SF/OPG-Fc mice had greater BV/TV than SF/VEH or GC/VEH. SF reduced femur elastic and maximum strength in VEH mice, with OPG-Fc increasing elastic strength in SF mice. Serum TRAP5b was elevated in SF/VEH mice vs. GC/VEH mice. Conversely, SF/OPG-Fc mice had lower TRAP5b levels, suggesting that OPG-Fc preserved bone during spaceflight via inhibition of osteoclast-mediated bone resorption. Decreased bone formation also contributed to the observed osteopenia, based on the reduced femur periosteal bone formation rate and serum osteocalcin level. Overall, these observations suggest that the beneficial effects of OPG-Fc during SF are primarily due to dramatic and sustained suppression of bone resorption. In growing mice, this effect appears to compensate for the SF-related inhibition of bone formation, while preventing any SF-related increase in bone resorption. We have demonstrated that the young mouse is an appropriate new model for SF-induced osteopenia, and that a single pre-flight treatment with OPG-Fc can effectively prevent the deleterious effects of SF on mouse bone.
Keywords: Bone loss; Countermeasure; Mice; Osteoprotegerin; Spaceflight.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Tesch PA, Berg HE, Bring D, Evans HJ, LeBlanc AD. Effects of 17-day spaceflight on knee extensor muscle function and size. Eur J Appl Physiol 2005;93: 463–8. - PubMed
-
- Zayzafoon M, Meyers VE, McDonald JM. Microgravity: the immune response and bone. Immunol Rev 2005;208: 267–80. - PubMed
-
- Markin AA, Zhuravleva OA, Morukov BV, Vostrikova LV, Zabolotskaia IV, Poluektova VP. [Characteristics of cosmonauts’ metabolism after extended missions on the international space station]. Aviakosm Ekolog Med 2005;39: 36–41. - PubMed
-
- Spector ER, Smith SM, Sibonga JD. Skeletal effects of long-duration head-down bed rest. Aviat Space Environ Med 2009;80: A23–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

