The inhibition of human farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase by nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates. Elucidating the role of active site threonine 201 and tyrosine 204 residues using enzyme mutants
- PMID: 26318908
- PMCID: PMC4652608
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.08.020
The inhibition of human farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase by nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates. Elucidating the role of active site threonine 201 and tyrosine 204 residues using enzyme mutants
Abstract
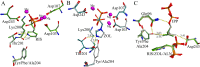
Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (FPPS) is the major molecular target of nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates (N-BPs), used clinically as bone resorption inhibitors. We investigated the role of threonine 201 (Thr201) and tyrosine 204 (Tyr204) residues in substrate binding, catalysis and inhibition by N-BPs, employing kinetic and crystallographic studies of mutated FPPS proteins. Mutants of Thr201 illustrated the importance of the methyl group in aiding the formation of the Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) binding site, while Tyr204 mutations revealed the unknown role of this residue in both catalysis and IPP binding. The interaction between Thr201 and the side chain nitrogen of N-BP was shown to be important for tight binding inhibition by zoledronate (ZOL) and risedronate (RIS), although RIS was also still capable of interacting with the main-chain carbonyl of Lys200. The interaction of RIS with the phenyl ring of Tyr204 proved essential for the maintenance of the isomerized enzyme-inhibitor complex. Studies with conformationally restricted analogues of RIS reaffirmed the importance of Thr201 in the formation of hydrogen bonds with N-BPs. In conclusion we have identified new features of FPPS inhibition by N-BPs and revealed unknown roles of the active site residues in catalysis and substrate binding.
Keywords: Active site mutant; Bisphosphonate; Drug binding; Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase; Inhibition mechanism; Substrate binding.
Copyright © 2015. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Buhaescu I., Izzedine H. Mevalonate pathway: a review of clinical and therapeutical implications. Clin. Biochem. 2007;40:575–584. - PubMed
-
- Dunford J.E., Thompson K., Coxon F.P., Luckman S.P., Hahn F.M., Poulter C.D., Ebetino F.H., Rogers M.J. Structure–activity relationships for inhibition of farnesyl diphosphate synthase in vitro and inhibition of bone resorption in vivo by nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001;296:235–242. - PubMed
-
- Rogers M.J., Gordon S., Benford H.L., Coxon F.P., Luckman S.P., Monkkonen J., Frith J.C. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates. Cancer. 2000;88:2961–2978. - PubMed
-
- Luckman S.P., Coxon F.P., Ebetino F.H., Russell R.G., Rogers M.J. Heterocycle-containing bisphosphonates cause apoptosis and inhibit bone resorption by preventing protein prenylation: evidence from structure–activity relationships in J774 macrophages. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1998;13:1668–1678. - PubMed
-
- Coxon F.P., Helfrich M.H., Van't Hof R., Sebti S., Ralston S.H., Hamilton A., Rogers M.J. Protein geranylgeranylation is required for osteoclast formation, function, and survival: inhibition by bisphosphonates and GGTI-298. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2000;15:1467–1476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

