Knockdown of Indy/CeNac2 extends Caenorhabditis elegans life span by inducing AMPK/aak-2
- PMID: 26318988
- PMCID: PMC4586101
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.100791
Knockdown of Indy/CeNac2 extends Caenorhabditis elegans life span by inducing AMPK/aak-2
Abstract
Reducing the expression of the Indy (Acronym for 'I'm Not Dead, Yet') gene in lower organisms promotes longevity and leads to a phenotype that resembles various aspects of caloric restriction. In C. elegans, the available data on life span extension is controversial. Therefore, the aim of this study was to determine the role of the C. elegans INDY homolog CeNAC2 in life span regulation and to delineate possible molecular mechanisms. siRNA against Indy/CeNAC2 was used to reduce expression of Indy/CeNAC2. Mean life span was assessed in four independent experiments, as well as whole body fat content and AMPK activation. Moreover, the effect of Indy/CeNAC2 knockdown in C. elegans with inactivating variants of AMPK (TG38) was studied. Knockdown of Indy/CeNAC2 increased life span by 22±3 % compared to control siRNA treated C. elegans, together with a decrease in whole body fat content by ~50%. Indy/CeNAC2 reduction also increased the activation of the intracellular energy sensor AMPK/aak2. In worms without functional AMPK/aak2, life span was not extended when Indy/CeNAC2 was reduced. Inhibition of glycolysis with deoxyglucose, an intervention known to increase AMPK/aak2 activity and life span, did not promote longevity when Indy/CeNAC2 was knocked down. Together, these data indicate that reducing the expression of Indy/CeNAC2 increases life span in C. elegans, an effect mediated at least in part by AMPK/aak2.
Keywords: AMPK; C.elegans; CeNAC-2; Indy; Slc13A5; aak-2; mIndy.
Conflict of interest statement
ALB owns shares of Eternygen GmbH. The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures
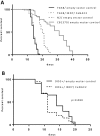
References
-
- Rogina B, et al. Extended life-span conferred by cotransporter gene mutations in Drosophila. Science. 2000;290:2137–2140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

